Page 343 - Phase Space Optics Fundamentals and Applications
P. 343
324 Chapter Ten
k k
W
b q x x
(a) (b)
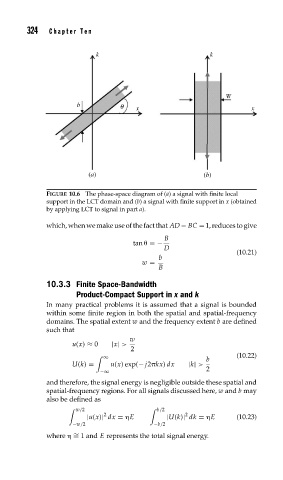
FIGURE 10.6 The phase-space diagram of (a) a signal with finite local
support in the LCT domain and (b) a signal with finite support in x (obtained
by applying LCT to signal in part a).
which,whenwemakeuseofthefactthat AD − BC = 1,reducestogive
B
tan =−
D
(10.21)
b
w =
B
10.3.3 Finite Space-Bandwidth
Product-Compact Support in x and k
In many practical problems it is assumed that a signal is bounded
within some finite region in both the spatial and spatial-frequency
domains. The spatial extent w and the frequency extent b are defined
such that
w
u(x) ≈ 0 |x| >
2
(10.22)
∞ b
U(k) = u(x) exp(− j2 kx) dx |k| >
2
−∞
and therefore, the signal energy is negligible outside these spatial and
spatial-frequency regions. For all signals discussed here, w and b may
also be defined as
w/2 b/2
2
2
|u(x)| dx = E |U(k)| dk = E (10.23)
−w/2 −b/2
where = 1 and E represents the total signal energy.
∼