Page 3 - Phase-Locked Loops Design, Simulation, and Applications
P. 3
INTRODUCTION TO PLLS Ronald E. Best 2
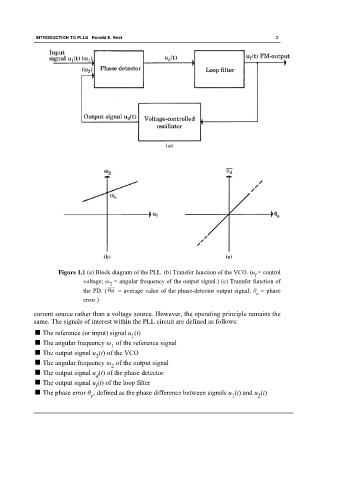
Figure 1.1 (a) Block diagram of the PLL. (b) Transfer function of the VCO. (u = control
f
voltage; ω = angular frequency of the output signal.) (c) Transfer function of
2
the PD. ( = average value of the phase-detector output signal; θ = phase
e
error.)
current source rather than a voltage source. However, the operating principle remains the
same. The signals of interest within the PLL circuit are defined as follows:
■ The reference (or input) signal u (t)
1
■ The angular frequency ω of the reference signal
1
■ The output signal u (t) of the VCO
2
■ The angular frequency ω of the output signal
2
■ The output signal u (t) of the phase detector
d
■ The output signal u (t) of the loop filter
f
■ The phase error θ , defined as the phase difference between signals u (t) and u (t)
e 1 2