Page 255 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 255
222 PHASE EQUILIBRIA
We can cancel the gas constant R, the volume and temperature, which are all constant,
to yield
p (total) = p (petrol) + p (oxygen) + p (nitrogen)
which is Dalton’s law, Equation (5.19).
How do anaesthetics work?
Gases dissolving in liquids: Henry’s law
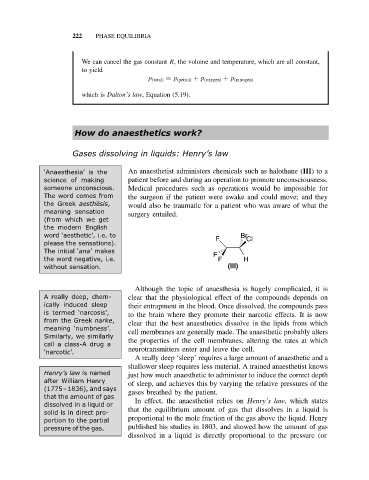
‘Anaesthesia’ is the An anaesthetist administers chemicals such as halothane (III)to a
science of making patient before and during an operation to promote unconsciousness.
someone unconscious. Medical procedures such as operations would be impossible for
The word comes from the surgeon if the patient were awake and could move; and they
the Greek aesthesis, would also be traumatic for a patient who was aware of what the
meaning sensation
surgery entailed.
(from which we get
the modern English
word ‘aesthetic’, i.e. to F Br Cl
please the sensations).
The initial ‘ana’makes F
the word negative, i.e. F H
without sensation. (III)
Although the topic of anaesthesia is hugely complicated, it is
A really deep, chem- clear that the physiological effect of the compounds depends on
ically induced sleep their entrapment in the blood. Once dissolved, the compounds pass
is termed ‘narcosis’, to the brain where they promote their narcotic effects. It is now
from the Greek narke, clear that the best anaesthetics dissolve in the lipids from which
meaning ‘numbness’. cell membranes are generally made. The anaesthetic probably alters
Similarly, we similarly
call a class-A drug a the properties of the cell membranes, altering the rates at which
‘narcotic’. neurotransmitters enter and leave the cell.
A really deep ‘sleep’ requires a large amount of anaesthetic and a
shallower sleep requires less material. A trained anaesthetist knows
Henry’s law is named just how much anaesthetic to administer to induce the correct depth
after William Henry of sleep, and achieves this by varying the relative pressures of the
(1775–1836), and says
gases breathed by the patient.
that the amount of gas In effect, the anaesthetist relies on Henry’s law, which states
dissolved in a liquid or
solid is in direct pro- that the equilibrium amount of gas that dissolves in a liquid is
portion to the partial proportional to the mole fraction of the gas above the liquid. Henry
pressure of the gas. published his studies in 1803, and showed how the amount of gas
dissolved in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure (or