Page 252 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 252
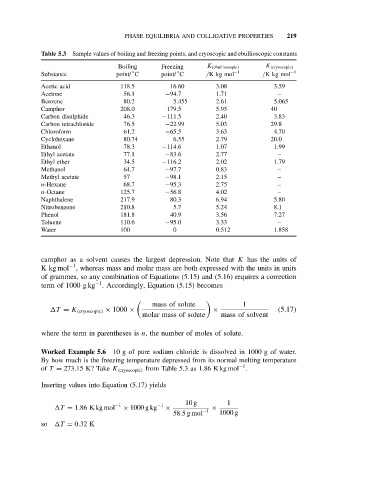
PHASE EQUILIBRIA AND COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES 219
Table 5.3 Sample values of boiling and freezing points, and cryoscopic and ebullioscopic constants
Boiling Freezing K (ebullioscopic) K (cryoscopic)
◦
◦
Substance point/ C point/ C /Kkgmol −1 /Kkgmol −1
Acetic acid 118.5 16.60 3.08 3.59
Acetone 56.1 −94.7 1.71 –
Benzene 80.2 5.455 2.61 5.065
Camphor 208.0 179.5 5.95 40
Carbon disulphide 46.3 −111.5 2.40 3.83
Carbon tetrachloride 76.5 −22.99 5.03 29.8
Chloroform 61.2 −65.5 3.63 4.70
Cyclohexane 80.74 6.55 2.79 20.0
Ethanol 78.3 −114.6 1.07 1.99
Ethyl acetate 77.1 −83.6 2.77 –
Ethyl ether 34.5 −116.2 2.02 1.79
Methanol 64.7 −97.7 0.83 –
Methyl acetate 57 −98.1 2.15 –
n-Hexane 68.7 −95.3 2.75 –
n-Octane 125.7 −56.8 4.02 –
Naphthalene 217.9 80.3 6.94 5.80
Nitrobenzene 210.8 5.7 5.24 8.1
Phenol 181.8 40.9 3.56 7.27
Toluene 110.6 −95.0 3.33 –
Water 100 0 0.512 1.858
camphor as a solvent causes the largest depression. Note that K has the units of
−1
Kkg mol , whereas mass and molar mass are both expressed with the units in units
of grammes, so any combination of Equations (5.15) and (5.16) requires a correction
−1
term of 1000 g kg . Accordingly, Equation (5.15) becomes
mass of solute 1
T = K (cryoscopic) × 1000 × × (5.17)
molarmassofsolute mass of solvent
where the term in parentheses is n, the number of moles of solute.
Worked Example 5.6 10 g of pure sodium chloride is dissolved in 1000 g of water.
By how much is the freezing temperature depressed from its normal melting temperature
−1
of T = 273.15 K? Take K (cryoscopic) from Table 5.3 as 1.86 K kg mol .
Inserting values into Equation (5.17) yields
10 g 1
−1
−1
T = 1.86 K kg mol × 1000 g kg × −1 ×
58.5g mol 1000 g
so T = 0.32 K