Page 398 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 398
Sample algorithms 1373
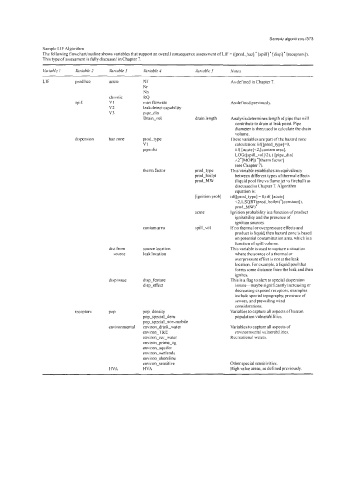
Sample LIFAlgorithm
The following flowchartioutline shows variables that support an overall consequence assessment of LIF = ([prod-haz] * [spill] * [disp] * [receptors]).
This type of assessment is fully discussed in Chapter 7.
Vuriahle I Vnriahle 2 Vnrrable 3 Chriable 4 Variable 5 Notes
LIF prod haz acute Nf As defined in Chapter 7
Nr
Nh
chronic RQ
spill VI max flowrate As defined previously.
v2 leak detect capability
v3 pipe-dia
Drain-vol drain length Analysis determines length ofpipe that will
contribute to drain at leak point. Pipe
diameter is then used to calculate the drain
volume.
dispersion haz zone prod-type These variables are part ofthe hazard zone
VI calculation: iif([prod-type]=O,
pipe dia iif( [acute]<2,[contam area],
LOG([spill-vol]/2), ( [pipe-dial
A~'[MOP]) '[therm factor]
(see Chapter 7).
them factor prod-type This variable establishes an equivalency
prod-hoilpt between different types ofthermal effects
prod-MW (liquid pool fire vs flame jet vs fireball) as
discussed in Chapter 7. Algorithm
equation is:
[ignition proh] iif([prod_type] = O,iif( [acute]
<2,1 ,SQRT(prod_boilpt)'[constant] ),
prod-MW)'
acute Ignition probability is a function ofproduct
ignitahility and the presence of
ignition sources.
contam area spill-vol Ifno thermal or overpressure effects and
product is liquid, then hazard zone is based
on potential contamination area, which is a
function of spill volume.
dist from source location This variable is used to capture a situation
\ource leak location where the source of a thermal or
overpressure effect is not at the leak
location. For example, a liquid pool that
forms some distance from the leak and then
ignites.
disp issue disp-feature This is a flag to alert to special dispersion
disp-effect issues-maybe significantly increasing or
decreasing exposed receptors; examples
include special topography, presence of
sewers, and prevailing wind
considerations.
receptors POP pop-density Variables to capture all aspects of human
pop-special-dens population vulnerabilities.
pop-special-non-mobile
environmental environ-drink-water Variables to capture all aspects of
environ-T&E environmental vulnerabilities.
environ-rec-water Recreational waters.
environ-prime-ag
environ-aquifer
environ-wetlands
environ-shoreline
environ-sensitive Other special sensitivities.
H VA HVA High value areas; as defined previously