Page 209 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 209
196 Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
for line protected by rectifiers; first investigating locations next checking potentials, and finally making a line current
where something has been done which might be responsible, survey.
Cathodic protection for pipelines
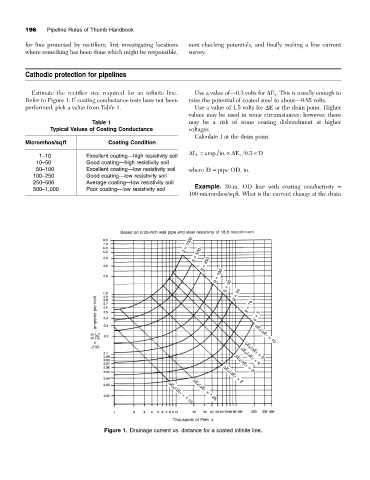
Estimate the rectifier size required for an infinite line. Use a value of—0.3 volts for DE x . This is usually enough to
Refer to Figure 1. If coating conductance tests have not been raise the potential of coated steel to about—0.85 volts.
performed, pick a value from Table 1. Use a value of 1.5 volts for DE at the drain point. Higher
values may be used in some circumstances; however, there
Table 1 may be a risk of some coating disbondment at higher
Typical Values of Coating Conductance voltages.
Calculate I at the drain point.
Micromhos/sqft Coating Condition
.
.
.
DI A = amp in ¥ DE x 03 ¥ D
1–10 Excellent coating—high resistivity soil
10–50 Good coating—high resistivity soil
50–100 Excellent coating—low resistivity soil where D = pipe OD, in.
100–250 Good coating—low resistivity soil
250–500 Average coating—low resistivity soil
Example. 30-in. OD line with coating conductivity =
500–1,000 Poor coating—low resistivity soil
100 micromhos/sqft. What is the current change at the drain
Figure 1. Drainage current vs. distance for a coated infinite line.