Page 212 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 212
Corrosion/Coatings 199
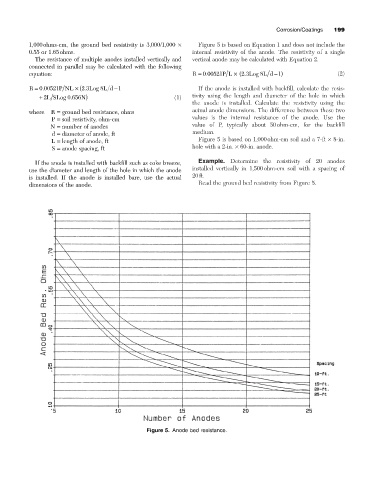
1,000ohms-cm, the ground bed resistivity is 3,000/1,000 ¥ Figure 5 is based on Equation 1 and does not include the
0.55 or 1.65ohms. internal resistivity of the anode. The resistivity of a single
The resistance of multiple anodes installed vertically and vertical anode may be calculated with Equation 2.
connected in parallel may be calculated with the following
.
.
8
equation: R = 0 00521 P L ¥ (2 3 Log L d - ) 1 (2)
.
.
8
R = 0 00521 P NL ¥ (2 3 Log L d -1 If the anode is installed with backfill, calculate the resis-
.
+ 2 L SLog 0 656 N) (1) tivity using the length and diameter of the hole in which
the anode is installed. Calculate the resistivity using the
where R = ground bed resistance, ohms actual anode dimensions. The difference between these two
P = soil resistivity, ohm-cm values is the internal resistance of the anode. Use the
N = number of anodes value of P, typically about 50ohm-cm, for the backfill
d = diameter of anode, ft medium.
L = length of anode, ft Figure 5 is based on 1,000ohm-cm soil and a 7-ft ¥ 8-in.
S = anode spacing, ft hole with a 2-in. ¥ 60-in. anode.
If the anode is installed with backfill such as coke breeze, Example. Determine the resistivity of 20 anodes
use the diameter and length of the hole in which the anode installed vertically in 1,500ohm-cm soil with a spacing of
is installed. If the anode is installed bare, use the actual 20ft.
dimensions of the anode. Read the ground bed resistivity from Figure 5.
Figure 5. Anode bed resistance.