Page 213 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 213
200 Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
R = 0.202ohm dard alloy or high purity alloy. Galvanic anodes are usually
pre-packaged with backfill to facilitate their installation. They
Since the anodes are to be installed in 1,500ohm-cm soil and may also be ordered bare if desired. Galvanic anodes offer the
Figure 5 is based on 1,000ohm-cm soil, multiply R by the advantage of more uniformly distributing the cathodic pro-
ratio of the actual soil resistivity to 1,000ohm-cm. tection current along the pipeline and it may be possible to
protect the pipeline with a smaller amount of current than
¥
,
,
R = 0 202 1 500 1 000 would be required with an impressed current system but not
.
necessarily at a lower cost. Another advantage is that inter-
R = 0.303ohm ference with other structures is minimized when galvanic
anodes are used.
The internal resistivity for a single 2-in. ¥ 60-in. vertical Galvanic anodes are not an economical source of cathodic
anode installed in 50ohm-cm backfill (7ft ¥ 8-in. hole) is protection current in areas of high soil resistivity. Their use is
0.106ohm. generally limited to soils of 3,000ohm-cm except where small
Since 20 anodes will be installed in parallel, divide the resis- amounts of current are needed.
tivity for one anode by the number of anodes to obtain the Magnesium is the most-used material for galvanic anodes
internal resistivity of the anode bank. for pipeline protection. Magnesium offers a higher solution
potential than zinc and may therefore be used in areas of
0 106 20 = 0 005ohm higher soil resistivity. A smaller amount of magnesium will
.
.
generally be required for a comparable amount of current.
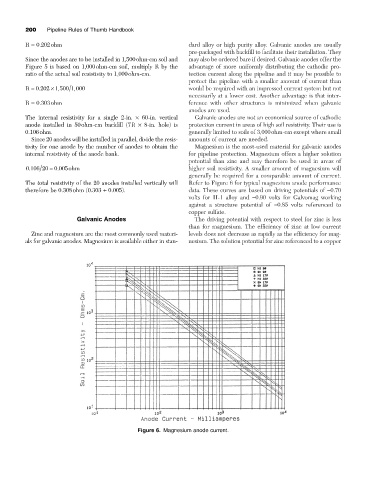
The total resistivity of the 20 anodes installed vertically will Refer to Figure 6 for typical magnesium anode performance
therefore be 0.308ohm (0.303 + 0.005). data. These curves are based on driving potentials of -0.70
volts for H-1 alloy and -0.90 volts for Galvomag working
against a structure potential of -0.85 volts referenced to
copper sulfate.
Galvanic Anodes The driving potential with respect to steel for zinc is less
than for magnesium. The efficiency of zinc at low current
Zinc and magnesium are the most commonly used materi- levels does not decrease as rapidly as the efficiency for mag-
als for galvanic anodes. Magnesium is available either in stan- nesium. The solution potential for zinc referenced to a copper
Figure 6. Magnesium anode current.