Page 282 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 282
Gas—Compression 269
Compressors
The following data are for use in the approximation of age of the volume swept by the piston in making its full deliv-
horsepower needed for compression of gas. ery stroke for the end of the cylinder being considered.
Ratio of compression is the ratio of the absolute dis-
charge pressure to the absolute inlet pressure.
Definitions Actual capacity is the quantity of gas compressed and
delivered, expressed in cubic ft per minute, at the intake pres-
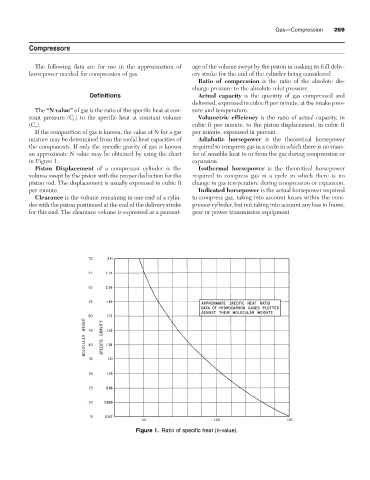
The “N value” of gas is the ratio of the specific heat at con- sure and temperature.
stant pressure (C p ) to the specific heat at constant volume Volumetric efficiency is the ratio of actual capacity, in
(C v ). cubic ft per minute, to the piston displacement, in cubic ft
If the composition of gas is known, the value of N for a gas per minute, expressed in percent.
mixture may be determined from the molal heat capacities of Adiabatic horsepower is the theoretical horsepower
the components. If only the specific gravity of gas is known required to compress gas in a cycle in which there is no trans-
an approximate N value may be obtained by using the chart fer of sensible heat to or from the gas during compression or
in Figure 1. expansion.
Piston Displacement of a compressor cylinder is the Isothermal horsepower is the theoretical horsepower
volume swept by the piston with the proper deduction for the required to compress gas in a cycle in which there is no
piston rod. The displacement is usually expressed in cubic ft change in gas temperature during compression or expansion.
per minute. Indicated horsepower is the actual horsepower required
Clearance is the volume remaining in one end of a cylin- to compress gas, taking into account losses within the com-
der with the piston positioned at the end of the delivery stroke pressor cylinder, but not taking into account any loss in frame,
for this end. The clearance volume is expressed as a percent- gear or power transmission equipment.
Figure 1. Ratio of specific heat (n-value).