Page 43 - Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
P. 43
30 Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook
Flooding for hydrotest
In order to demonstrate the strength and integrity of the high points. Even with a pig, in mountainous terrain with
the pipeline, it is filled with water and pressure tested. The steep downhill slopes, the weight of water behind the pig can
air must be removed so that the line can be pressurized effi- cause it to accelerate away leaving a low pressure zone at the
ciently because, if pockets of air remain, these will be com- hill crest. This would cause dissolved air to come out of solu-
pressed and absorb energy. It will also take longer to bring tion and form an air lock. A pig with a high pressure drop
the line up to pressure and will be more hazardous in the across it would be required to prevent this.
event of a rupture during the test. It is therefore necessary to Alternatives to using a pig include flushing out the air or
ensure that the line is properly flooded and all of the air is installing vents at high point. For a long or large-diameter
displaced. pipeline achieving sufficient flushing velocity becomes
A batching pig driven ahead of the water forms an efficient impractical. Installing vents reduces the pipeline integrity and
interface. Without a pig, in downhill portions of the line, the should be avoided. So for flooding a pipeline, pigging is nor-
water will run down underneath the air trapping pockets at mally the best solution.
Dewatering and drying
After the hydrotest has been completed, the water is gen- required for chemical pipelines such as ethylene and propyl-
erally displaced by the product or by nitrogen. The same argu- ene pipelines since water will contaminate the material and
ments apply to dewatering as to flooding. A pig is used to make it unuseable. After dewatering the pipe walls will be
provide an interface between the hydrotest water and the damp and some water may remain trapped in valves and dead
displacing medium so that the water is swept out of all low legs. This problem is solved by designing dead legs to be self
points. A bidirectional batching pig may be used during draining and installing drain on valves.
hydrotest and left in the line during hydrotest and then Refer to Chapter 5, Pipeline Drying, for a detailed dis-
reversed to dewater the line. cussing of pipeline drying methods.
In some cases, it may be necessary to dry the pipeline. This
is particularily so for gas pipelines where traces of water Reprinted with permission—Gulf Publishing Co. “Pipeline Pigging
may combine with the gas to form hydrates. Drying is also Technology 2nd Edition”
Estimate volume of onshore oil spill
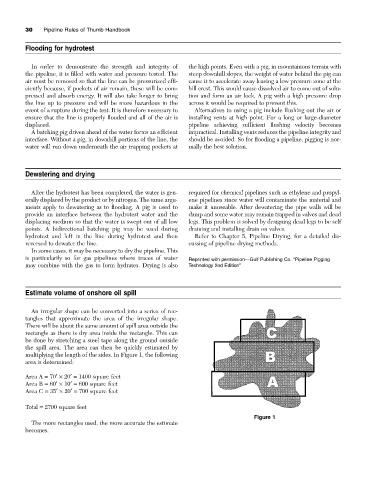
An irregular shape can be converted into a series of rec-
tangles that approximate the area of the irregular shape.
There will be about the same amount of spill area outside the
rectangle as there is dry area inside the rectangle. This can
be done by stretching a steel tape along the ground outside
the spill area. The area can then be quickly estimated by
multiplying the length of the sides. In Figure 1, the following
area is determined:
Area A = 70¢¥ 20¢= 1400 square feet
Area B = 60¢¥ 10¢= 600 square feet
Area C = 35¢¥ 20¢= 700 square feet
Total = 2700 square feet
Figure 1
The more rectangles used, the more accurate the estimate
becomes.