Page 272 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 272
Remaining Strength of Corroded Pipes 245
14.5.4 Safety Level in the B31G Criteria
Reliability methods are applied to estimate the implied safety level of the B31G criterion. The
uncertainties described in the section 14.6.3 are used in the reliability analysis. The safety
factor is taken as 1.4 in the B31G criteria.
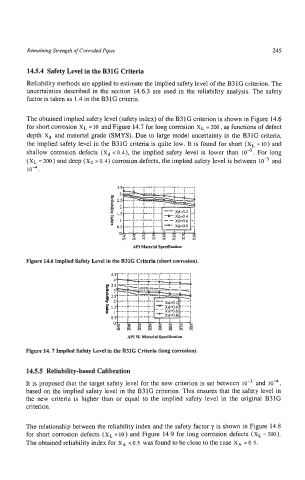
The obtained implied safety level (safety index) of the B31G criterion is shown in Figure 14.6
for short corrosion XL = 10 and Figure 14.7 for long corrosion XL = 200, as functions of defect
depth xd and material grade (SMYS). Due to large model uncertainty in the B31G criteria,
the implied safety level in the B31G criteria is quite low. It is found for short (xL =io) and
shallow corrosion defects (X, c 0.4), the implied safety level is lower than For long
(XL = 200) and deep (xd > 0.4) corrosion defects, the implied safety level is between and
IO”.
.....
....
_._
....
API Material Speeiticalim
Figure 14.6 Implied Safety Level in the B31G Criteria (short corrosion).
...................................
! ! ! ! ! !
Figure 14.7 Implied Safety Level in the B31G Criteria (long corrosion).
14.5.5 Reliability-based Calibration
It is proposed that the target safety level for the new criterion is set between 10” and IO“,
based on the implied safety level in the B31G criterion. This ensures that the safety level in
the new criteria is higher than or equal to the implied safety level in the original B31G
criterion.
The relationship between the reliability index and the safety factory is shown in Figure 14.8
for short corrosion defects (X, = 10) and Figure 14.9 for long corrosion defects (X, = 200).
The obtained reliability index for XA < 0.5 was found to be close to the case XA = 0.5.