Page 273 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 273
246 Chapter 14
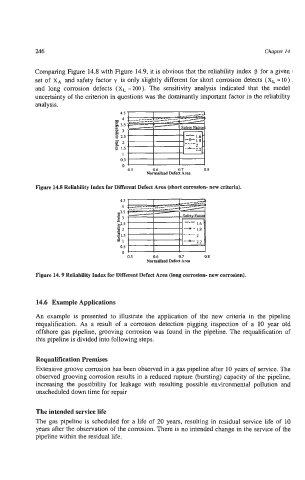
Comparing Figure 14.8 with Figure 14.9, it is obvious that the reliability index p for a given
set of xA and safety factor y is only slightly different for short corrosion detects (X, = 10)
and long corrosion defects (X, =ZOO). The sensitivity analysis indicated that the model
uncertainty of the criterion in questions was the dominantly important factor in the reliability
analysis.
";; -
7.-
4
!! 3.5
53
5 2.5
22
:: 1.5
1
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
NdiadDelectArea
1
Figure 14.8 Reliability Index for Different Defect Area (short corrosion- new criteria).
3.5 rl---
z2 _.....
--
:6
---- 1.8
Tl.5
a1 2.2
0.5
0
0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
Normaliad Defect Area
Figure 14.9 Reliability Index for Different Defect Area (long corrosion- new corrosion).
14.6 Example Applications
An example is presented to illustrate the application of the new criteria in the pipeline
requalification. As a result of a corrosion detection pigging inspection of a 10 year old
offshore gas pipeline, grooving corrosion was found in the pipeline. The requalification of
this pipeline is divided into following steps.
Requalification Premises
Extensive groove corrosion has been observed in a gas pipeline after 10 years of service. The
observed grooving corrosion results in a reduced rupture (bursting) capacity of the pipeline,
increasing the possibility for leakage with resulting possible environmental pollution and
unscheduled down time for repair
The intended service life
The gas pipeline is scheduled for a life of 20 years, resulting in residual service life of 10
years after the observation of the corrosion. There is no intended change in the service of the
pipeline within the residual life.