Page 380 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 380
Pipeline inspection, Maintenance and Repair 35 1
A
L’
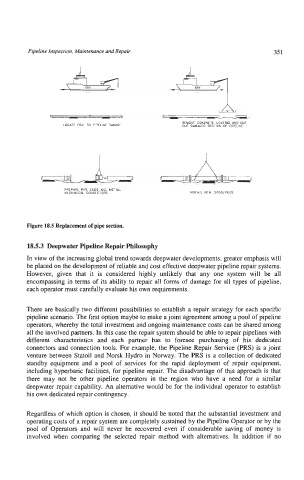
REMOVE CONCRETE COATING AND CUT
LOCATE OSV TO PIPELINE DAMAGE OUT DAMAGED SECTION OF PIPELINE
PREPARE PIPE ENDS AND INSTALL
MECHANICAL CONNECTORS INSTALL NEW SPOOLPIECE
Figure 18.5 Replacement of pipe section.
18.5.3 Deepwater Pipeline Repair Philosophy
In view of the increasing global trend towards deepwater developments, greater emphasis will
be placed on the development of reliable and cost effective deepwater pipeline repair systems.
However, given that it is considered highly unlikely that any one system will be all
encompassing in terms of its ability to repair all forms of damage for all types of pipeline,
each operator must carefully evaluate his own requirements.
There are basically two different possibilities to establish a repair strategy for each specific
pipeline scenario. The first option maybe to make a joint agreement among a pool of pipeline
operators, whereby the total investment and ongoing maintenance costs can be shared among
all the involved partners. In this case the repair system should be able to repair pipelines with
different characteristics and each partner has to foresee purchasing of his dedicated
connectors and connection tools. For example, the Pipeline Repair Service (PRS) is a joint
venture between Statoil and Norsk Hydro in Norway. The PRS is a collection of dedicated
standby equipment and a pool of services for the rapid deployment of repair equipment,
including hyperbaric facilities, for pipeline repair. The disadvantage of this approach is that
there may not be other pipeline operators in the region who have a need for a similar
deepwater repair capability. An alternative would be for the individual operator to establish
his own dedicated repair contingency.
Regardless of which option is chosen, it should be noted that the substantial investment and
operating costs of a repair system are completely sustained by the Pipeline Operator or by the
pool of Operators and will never be recovered even if considerable saving of money is
involved when comparing the selected repair method with alternatives. In addition if no