Page 441 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 441
408 Chapter 21
Comparison is performed for:
The moment for failure based on the Hauch & Bai (1999).
Allowable moments (including utilization factors) for each of the three approaches. For
the MI approach, based on allowable stresses, FEA analysis is performed to quantify the
equivalent moments for the allowable stress limit. The utilization factors used for each
approach are summarized in Table 21.7.
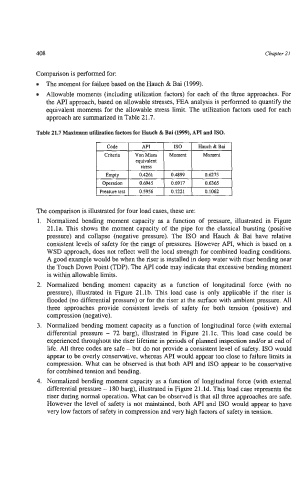
Table 21.7 Maxiinnun utilization factors for Hauch & Bai (1999), API and ISO.
I Code 1 API 1 IS0 I Hauch&Bai 1
Moment
equivalent
0.4261 0.4899 0.6275
The comparison is illustrated for four load cases, these are:
1. Normalized bending moment capacity as a function of pressure, illustrated in Figure
21.la. This shows the moment capacity of the pipe for the classical bursting (positive
pressure) and collapse (negative pressure). The IS0 and Hauch & Bai have relative
consistent levels of safety for the range of pressures. However MI, which is based on a
WSD approach, does not reflect well the local strength for combined loading conditions.
A good example would be when the riser is installed in deep water with riser bending near
the Touch Down Point (TDP). The API code may indicate that excessive bending moment
is within allowable limits.
2. Normalized bending moment capacity as a function of longitudinal force (with no
pressure), illustrated in Figure 21.lb. This load case is only applicable if the riser is
flooded (no differential pressure) or for the riser at the surface with ambient pressure. All
three approaches provide consistent levels of safety for both tension (positive) and
compression (negative).
3. Normalized bending moment capacity as a function of longitudinal force (with external
differential pressure - 72 barg), illustrated in Figure 21.1~. This load case could be
experienced throughout the riser lifetime in periods of planned inspection andor at end of
life. All three codes are safe - but do not provide a consistent level of safety. IS0 would
appear to be overly conservative, whereas API would appear too close to failure limits in
compression. What can be observed is that both API and IS0 appear to be conservative
for combined tension and bending.
4. Normalized bending moment capacity as a function of longitudinal force (with external
differential pressure - 180 barg), illustrated in Figure 21.ld. This load case represents the
riser during normal operation. What can be observed is that all three approaches are safe.
However the level of safety is not maintained, both API and IS0 would appear to have
very low factors of safety in compression and very high factors of safety in tension.