Page 460 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 460
Fatigue of Risers 427
Damage rate with strakes
~
1-With strakes
1 0 BOTTOM 04 WL 06 08 TOP 1
02
Fatigue life with strakes
400
e
E
200
0
0 02 04 06 08 t
BOTTOM XR TOP
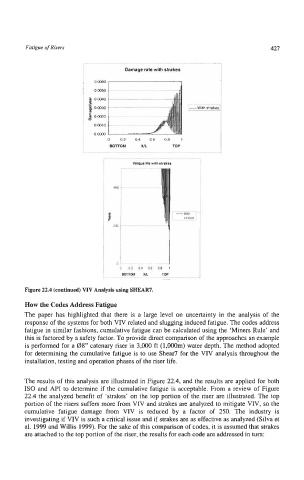
Figure 22.4 (continued) VIV Analysis using SHEAR7.
How the Codes Address Fatigue
The paper has highlighted that there is a large level on uncertainty in the analysis of the
response of the systems for both VIV related and slugging induced fatigue. The codes address
fatigue in similar fashions, cumulative fatigue can be calculated using the ‘Miners Rule’ and
this is factored by a safety factor. To provide direct comparison of the approaches an example
is performed for a 08” catenary riser in 3,000 ft (1,ooOm) water depth. The method adopted
for determining the cumulative fatigue is to use Shear7 for the VIV analysis throughout the
installation, testing and operation phases of the riser life.
The results of this analysis are illustrated in Figure 22.4, and the results are applied for both
IS0 and API to determine if the cumulative fatigue is acceptable. From a review of Figure
22.4 the analyzed benefit of ‘strakes’ on the top portion of the riser are illustrated. The top
portion of the risers suffers more from VIV and strakes are analyzed to mitigate VIV, so the
cumulative fatigue damage from VIV is reduced by a factor of 250. The industry is
investigating if VIV is such a critical issue and if strakes are as effective as analyzed (Silva et
al. 1999 and Willis 1999). For the sake of this comparison of codes, it is assumed that strakes
are attached to the top portion of the riser, the results for each code are addressed in turn: