Page 268 - Planning and Design of Airports
P. 268
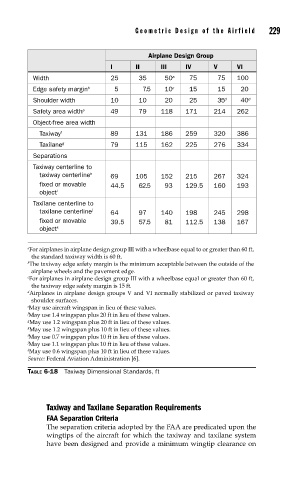
Geometric Design of the Airfield 229
Airplane Design Group
I II III IV V VI
Width 25 35 50 a 75 75 100
Edge safety margin b 5 7.5 10 c 15 15 20
Shoulder width 10 10 20 25 35 d 40 d
Safety area width e 49 79 118 171 214 262
Object-free area width
Taxiway f 89 131 186 259 320 386
Taxilane g 79 115 162 225 276 334
Separations
Taxiway centerline to
taxiway centerline h 69 105 152 215 267 324
fixed or movable 44.5 62.5 93 129.5 160 193
object i
Taxilane centerline to
taxilane centerline j 64 97 140 198 245 298
fixed or movable 39.5 57.5 81 112.5 138 167
object k
a For airplanes in airplane design group III with a wheelbase equal to or greater than 60 ft,
the standard taxiway width is 60 ft.
b The taxiway edge safety margin is the minimum acceptable between the outside of the
airplane wheels and the pavement edge.
c For airplanes in airplane design group III with a wheelbase equal or greater than 60 ft,
the taxiway edge safety margin is 15 ft.
d Airplanes in airplane design groups V and VI normally stabilized or paved taxiway
shoulder surfaces.
e May use aircraft wingspan in lieu of these values.
f May use 1.4 wingspan plus 20 ft in lieu of these values.
g May use 1.2 wingspan plus 20 ft in lieu of these values.
h May use 1.2 wingspan plus 10 ft in lieu of these values.
i May use 0.7 wingspan plus 10 ft in lieu of these values.
j May use 1.1 wingspan plus 10 ft in lieu of these values.
k May use 0.6 wingspan plus 10 ft in lieu of these values.
Source: Federal Aviation Administration [6].
TABLE 6-18 Taxiway Dimensional Standards, ft
Taxiway and Taxilane Separation Requirements
FAA Separation Criteria
The separation criteria adopted by the FAA are predicated upon the
wingtips of the aircraft for which the taxiway and taxilane system
have been designed and provide a minimum wingtip clearance on