Page 297 - Planning and Design of Airports
P. 297
258 Airp o r t D e sign
typically found at airports, although often there are preferences to a
given type of pavement depending on such factors as the type and
frequency of aircraft usage, climatic conditions, and costs of construc-
tion and maintenance.
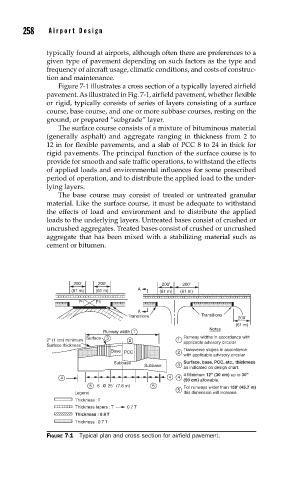
Figure 7-1 illustrates a cross section of a typically layered airfield
pavement. As illustrated in Fig. 7-1, airfield pavement, whether flexible
or rigid, typically consists of series of layers consisting of a surface
course, base course, and one or more subbase courses, resting on the
ground, or prepared “subgrade” layer.
The surface course consists of a mixture of bituminous material
(generally asphalt) and aggregate ranging in thickness from 2 to
12 in for flexible pavements, and a slab of PCC 8 to 24 in thick for
rigid pavements. The principal function of the surface course is to
provide for smooth and safe traffic operations, to withstand the effects
of applied loads and environmental influences for some prescribed
period of operation, and to distribute the applied load to the under-
lying layers.
The base course may consist of treated or untreated granular
material. Like the surface course, it must be adequate to withstand
the effects of load and environment and to distribute the applied
loads to the underlying layers. Untreated bases consist of crushed or
uncrushed aggregates. Treated bases consist of crushed or uncrushed
aggregate that has been mixed with a stabilizing material such as
cement or bitumen.
200' 200' 200' 200'
(61 m) (61 m) A (61 m) (61 m)
P1 P1
A
Transitions Transitions 200'
(61 m)
Notes
Runway width 1
Surface 3 Runway widths in accordance with
2'' (1 cm) minimum 2 1 applicable advisory circular
Surface thickness
Transverse slopes in accordance
Base PCC 2
with applicable advisory circular
Subbase Surface, base, PCC, etc., thickness
Subbase 3
as indicated on design chart.
4 Minimum 12'' (30 cm) up to 30''
4 4 4
(90 cm) allowable.
5 6 @ 25' (7.6 m) 5 For runways wider than 150' (45.7 m)
5
Legend this dimension will increase.
Thickness : T
Thickness tapers : T 0.7 T
Thickness : 0.9 T
Thickness : 0.7 T
FIGURE 7-1 Typical plan and cross section for airfi eld pavement.