Page 48 - Plastics Engineering
P. 48
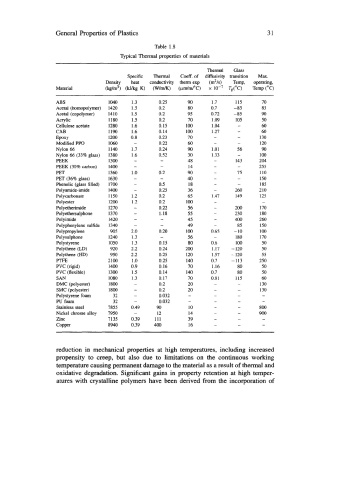
General Properties of Plastics 31
Table 1.8
TLP icd Thermd properties of materials
Thermal Glass
Specific Thermal Coeff . of diffusivity transition Max.
Density heat conductivity therm exp (m2/s) Temp, operating,
Material (kg/m3) Wkg K) (WIM) (ClmlmpC) IO-' TJC) Temp ("C)
ABS 1040 I .3 0.25 90 1.7 115 70
Acetal (homopolymer) 1420 1.5 0.2 80 0.7 -85 85
Acetal (copdymer) 1410 I .5 0.2 95 0.72 -85 90
Acrylic 1180 1.5 0.2 70 1.09 105 50
Cellulose acetate 1280 16 0.15 100 1.04 1c 60
-
CAB 1190 1.6 0.14 100 27 - 60
EPOXY 1200 0.8 0.23 70 - 130
Modified PPO 1060 0.22 60 - 4 120
Nylon 66 1 I40 1.7 0.24 90 + Ul 56 90
Nylon 66 (33% glass) 1380 1,6 0.52 30 1 &33 M 100
PEEK 1300 - - 48 I43 204
PEEK (30% carbon) 1400 - - 14 Iy 255
PET 1360 1 .o 0.2 90 75 110
PET (36% glass) 1630 - 40 d 150
Phenolic (glass filled) 1700 - 0.5 18 - 185
Poly amide-imide 1400 - 0.25 36 260 220
Polycarbonate 1150 1.2 Ob2 65 1.47 149 125
Polyester 1200 1.2 0.2 100 -
Pol yetherimide 1270 - 0.22 56 200 170
Poi yethersulphone 1370 - 1.18 55 230 180
Polyimide 1420 - - 45 40 260
Polyphenylene sulfide 1340 - - 49 85 150
Polypropylene 905 2.0 0.20 €00 0.65 - 10 1 0
Polysulphone 1240 1.3 - 56 180 170
Polystyrene 1050 1.3 0.15 80 0-6 100 50
Polythene (LD) 920 2.2 0.24 200 1.17 -120 50
Polythene (HP) 950 2.2 0.25 120 1.57 -120 55
PTFE 2100 1 .o 0.25 140 0.7 -1 13 250
PVC (igid) 1400 0.9 0.16 70 80 50
PVC (flexible) 1300 1 .$ 0.14 140 0.7 80 50
SAN 1080 1.3 0.17 70 0.81 115 60
DMC (plyester) 1800 - 0.2 20 - 130
SMC (polyester) 1800 - 0.2 20 - 130
Polystyrene foam 32 - 0.032 YL - -
PU foam 32 - 0.032 - -
Stainless steel 7855 0,49 90 10 - 800
Nickel chrome alloy 7950 -r 12 14 - 900
Zinc 7135 0.39 111 39 7 -
8940 0.39 400 16 lrrr -
reduction in mechanical properties at high temperatures, including increased
propensity to creep, but also due to limitations on the continuous working
temperature causing permanent damage to the material as a result of thermal and
oxidative degradation. Significant gains in property retentiun at high temper-
atures with crystalline polymers have been derived fmrn the incorporation of