Page 317 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 317
286 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
(Acidic/basic/neutral) (Simple/Mixed oxides)
Ceramics
(Nano/microscale) (Glass)
(Bio source) (Plant source)
Naturally sourced
materials
(Metal organic frameworks)
Porous
materials Fillers
(Mesoporous)
Fillers
Layered
clay
Polymer matrix Additives
Lithium salt Processing
Polymer composite electrolyte
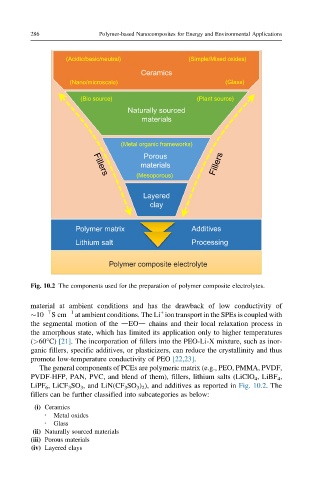
Fig. 10.2 The components used for the preparation of polymer composite electrolytes.
material at ambient conditions and has the drawback of low conductivity of
+
10 7 Scm 1 at ambient conditions. The Li ion transport in the SPEs is coupled with
the segmental motion of the dEOd chains and their local relaxation process in
the amorphous state, which has limited its application only to higher temperatures
(>60°C) [21]. The incorporation of fillers into the PEO-Li-X mixture, such as inor-
ganic fillers, specific additives, or plasticizers, can reduce the crystallinity and thus
promote low-temperature conductivity of PEO [22,23].
The general components of PCEs are polymeric matrix (e.g., PEO, PMMA, PVDF,
PVDF-HFP, PAN, PVC, and blend of them), fillers, lithium salts (LiClO 4 , LiBF 4 ,
LiPF 6 , LiCF 3 SO 3 , and LiN(CF 3 SO 3 ) 2 ), and additives as reported in Fig. 10.2.The
fillers can be further classified into subcategories as below:
(i) Ceramics
Metal oxides
l
l Glass
(ii) Naturally sourced materials
(iii) Porous materials
(iv) Layered clays