Page 38 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 38
Introduction of polymer-based nanocomposites 17
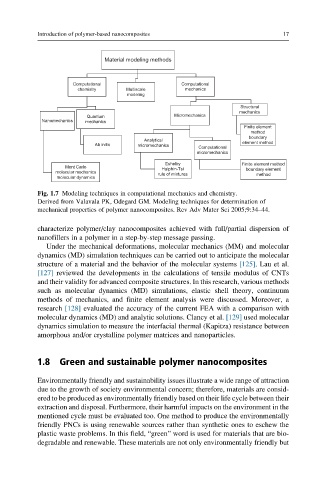
Material modeling methods
Computational Computational
chemistry Multiscale mechanics
modeling
Structural
mechanics
Quantum Micromechanics
Nanomechanics mechanics
Finite element
method
boundary
Analytical
Ab initio micromechanics element method
Computational
micromechanics
Eshelby Finite element method
Mont Carlo Halphin-Tsi boundary element
molecular mechanics rule of mixtures method
molecular dynamics
Fig. 1.7 Modeling techniques in computational mechanics and chemistry.
Derived from Valavala PK, Odegard GM. Modeling techniques for determination of
mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites. Rev Adv Mater Sci 2005;9:34–44.
characterize polymer/clay nanocomposites achieved with full/partial dispersion of
nanofillers in a polymer in a step-by-step message passing.
Under the mechanical deformations, molecular mechanics (MM) and molecular
dynamics (MD) simulation techniques can be carried out to anticipate the molecular
structure of a material and the behavior of the molecular systems [125]. Lau et al.
[127] reviewed the developments in the calculations of tensile modulus of CNTs
and their validity for advanced composite structures. In this research, various methods
such as molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, elastic shell theory, continuum
methods of mechanics, and finite element analysis were discussed. Moreover, a
research [128] evaluated the accuracy of the current FEA with a comparison with
molecular dynamics (MD) and analytic solutions. Clancy et al. [129] used molecular
dynamics simulation to measure the interfacial thermal (Kapitza) resistance between
amorphous and/or crystalline polymer matrices and nanoparticles.
1.8 Green and sustainable polymer nanocomposites
Environmentally friendly and sustainability issues illustrate a wide range of attraction
due to the growth of society environmental concern; therefore, materials are consid-
ered to be produced as environmentally friendly based on their life cycle between their
extraction and disposal. Furthermore, their harmful impacts on the environment in the
mentioned cycle must be evaluated too. One method to produce the environmentally
friendly PNCs is using renewable sources rather than synthetic ones to eschew the
plastic waste problems. In this field, “green” word is used for materials that are bio-
degradable and renewable. These materials are not only environmentally friendly but