Page 405 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 405
362 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
The third-generation solar cells are potential candidates to overcome limits of the previous
l
two generations. Among them, dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) are widely investigated due
to their economic advantages. This type of cells was firstly developed by O’Regan and
Gr€ atzel in 1991 [6]. Their working mechanism is very similar to the plant photosynthesis
in nature. Low raw material costs, processing methods with simple and inexpensive equip-
ment, and use of environmentally friendly materials make this technology very attractive.
13.2 Dye-sensitized solar cell
DSCs are one type of third-generation solar cells that are based on the generation of
exciton-electron-hole pairs-mechanism. After the first report by Gr€ atzel [6], more than
1
17,000 research articles have been reported to date. Facile fabrication, lower mate-
rials and equipment cost, and possibility to fabricate flexible solar cells are some
outstanding features of DSCs [7,8].
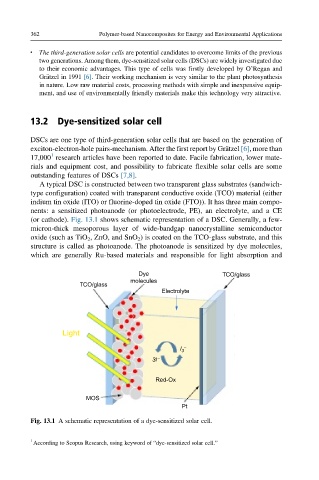
A typical DSC is constructed between two transparent glass substrates (sandwich-
type configuration) coated with transparent conductive oxide (TCO) material (either
indium tin oxide (ITO) or fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO)). It has three main compo-
nents: a sensitized photoanode (or photoelectrode, PE), an electrolyte, and a CE
(or cathode). Fig. 13.1 shows schematic representation of a DSC. Generally, a few-
micron-thick mesoporous layer of wide-bandgap nanocrystalline semiconductor
oxide (such as TiO 2 , ZnO, and SnO 2 ) is coated on the TCO-glass substrate, and this
structure is called as photoanode. The photoanode is sensitized by dye molecules,
which are generally Ru-based materials and responsible for light absorption and
Dye TCO/glass
molecules
TCO/glass
Electrolyte
Light
l 3 −
3l −
Red-Ox
MOS
Pt
Fig. 13.1 A schematic representation of a dye-sensitized solar cell.
1
According to Scopus Research, using keyword of “dye-sensitized solar cell.”