Page 526 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 526
Polypyrrole-based nanocomposite adsorbents 479
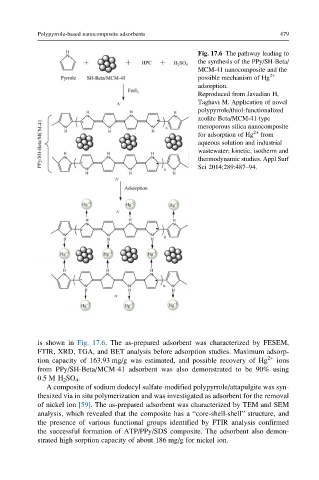
Fig. 17.6 The pathway leading to
the synthesis of the PPy/SH-Beta/
MCM-41 nanocomposite and the
possible mechanism of Hg 2+
adsorption.
Reproduced from Javadian H,
Taghavi M. Application of novel
polypyrrole/thiol-functionalized
zeolite Beta/MCM-41 type
mesoporous silica nanocomposite
for adsorption of Hg 2+ from
aqueous solution and industrial
wastewater: kinetic, isotherm and
thermodynamic studies. Appl Surf
Sci 2014;289:487–94.
is shown in Fig. 17.6. The as-prepared adsorbent was characterized by FESEM,
FTIR, XRD, TGA, and BET analysis before adsorption studies. Maximum adsorp-
tion capacity of 163.93 mg/g was estimated, and possible recovery of Hg 2+ ions
from PPy/SH-Beta/MCM-41 adsorbent was also demonstrated to be 90% using
0.5 M H 2 SO 4 .
A composite of sodium dodecyl sulfate-modified polypyrrole/attapulgite was syn-
thesized via in situ polymerization and was investigated as adsorbent for the removal
of nickel ion [59]. The as-prepared adsorbent was characterized by TEM and SEM
analysis, which revealed that the composite has a “core-shell-shell” structure, and
the presence of various functional groups identified by FTIR analysis confirmed
the successful formation of ATP/PPy/SDS composite. The adsorbent also demon-
strated high sorption capacity of about 186 mg/g for nickel ion.