Page 619 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 619
Polymer nanocomposites for water treatments 571
engineered nanostructured materials, much attention has been paid to nanocomposites
particularly polymer nanocomposites [11]. Nanocomposites have better adsorption
capacity, selectivity, and stability than nanoparticles (NPs) for water remediation.
A great variety of conductive polymer nanocomposites have been synthesized by
using the advanced technologies, such as solution blending, melt blending, layer-
by-layer deposition, in situ polymerization, electropolymerization, and surface-
initiated polymerization techniques. Now, polymer nanocomposites are being used
in different ways for the removal of contaminants from water [12–16]. In this chapter,
we provide an overview of recent advances on the use of polymer nanocomposites in
water remediation.
21.2 Water pollutants
Water pollution can be categorized into two different groups:
(i) Point sources. Factories, sewage system, power plants, underground coalmines, oil wells,
etc. Industrial activities release about 300–400 million tons of heavy metals, solvents, toxic
sludge, and other wastes into the global water each year, posing a great threat to human
beings.
(ii) Nonpoint sources. Nonpoint sources are diffused across a broad area, and their contamina-
tion cannot be traced to a single discharge point.
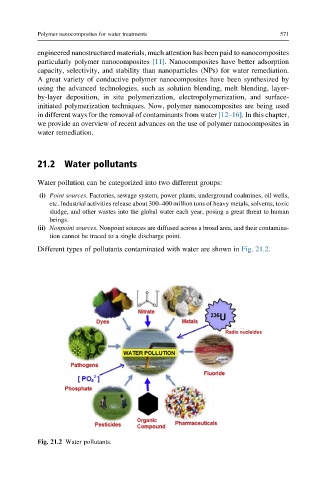
Different types of pollutants contaminated with water are shown in Fig. 21.2.
Fig. 21.2 Water pollutants.