Page 620 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 620
572 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
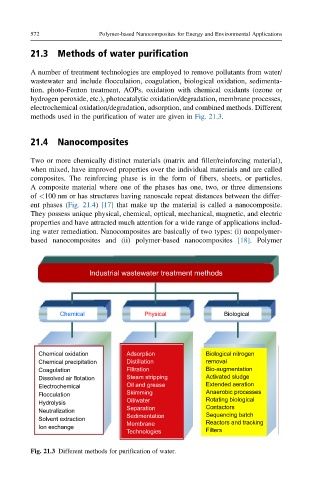
21.3 Methods of water purification
A number of treatment technologies are employed to remove pollutants from water/
wastewater and include flocculation, coagulation, biological oxidation, sedimenta-
tion, photo-Fenton treatment, AOPs, oxidation with chemical oxidants (ozone or
hydrogen peroxide, etc.), photocatalytic oxidation/degradation, membrane processes,
electrochemical oxidation/degradation, adsorption, and combined methods. Different
methods used in the purification of water are given in Fig. 21.3.
21.4 Nanocomposites
Two or more chemically distinct materials (matrix and filler/reinforcing material),
when mixed, have improved properties over the individual materials and are called
composites. The reinforcing phase is in the form of fibers, sheets, or particles.
A composite material where one of the phases has one, two, or three dimensions
of <100 nm or has structures having nanoscale repeat distances between the differ-
ent phases (Fig. 21.4) [17] that make up the material is called a nanocomposite.
They possess unique physical, chemical, optical, mechanical, magnetic, and electric
properties and have attracted much attention for a wide range of applications includ-
ing water remediation. Nanocomposites are basically of two types: (i) nonpolymer-
based nanocomposites and (ii) polymer-based nanocomposites [18]. Polymer
Industrial wastewater treatment methods
Chemical Physical Biological
Chemical oxidation Adsorption Biological nitrogen
Chemical precipitation Distillation removal
Coagulation Filtration Bio-augmentation
Dissolved air flotation Steam stripping Activated sludge
Electrochemical Oil and grease Extended aeration
Flocculation Skimming Anaerobic processes
Oil/water Rotating biological
Hydrolysis
Separation Contactors
Neutralization
Sedimentation Sequencing batch
Solvent extraction
Membrane Reactors and tracking
Ion exchange
Technologies Filters
Fig. 21.3 Different methods for purification of water.