Page 622 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 622
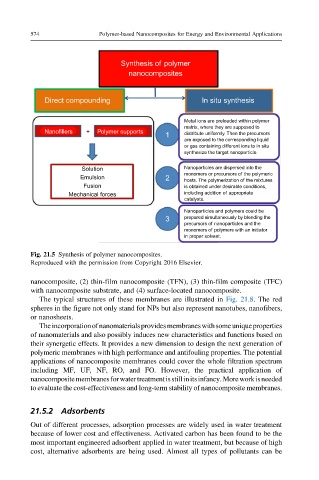
574 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
Synthesis of polymer
nanocomposites
Direct compounding In situ synthesis
Metal ions are preloaded within polymer
matrix, where they are supposed to
Nanofillers + Polymer supports
1 distribute uniformly. Then the precursors
are exposed to the corresponding liquid
or gas containing different ions to in situ
synthesize the target nanoparticle.
Solution Nanoparticles are dispersed into the
monomers or precursors of the polymeric
Emulsion 2 hosts. The polymerization of the mixtures
Fusion is obtained under desirable conditions,
Mechanical forces including addition of appropriate
catalysts.
Nanoparticles and polymers could be
3 prepared simultaneously by blending the
precursors of nanoparticles and the
monomers of polymers with an initiator
in proper solvent.
Fig. 21.5 Synthesis of polymer nanocomposites.
Reproduced with the permission from Copyright 2016 Elsevier.
nanocomposite, (2) thin-film nanocomposite (TFN), (3) thin-film composite (TFC)
with nanocomposite substrate, and (4) surface-located nanocomposite.
The typical structures of these membranes are illustrated in Fig. 21.8. The red
spheres in the figure not only stand for NPs but also represent nanotubes, nanofibers,
or nanosheets.
Theincorporationofnanomaterialsprovidesmembraneswithsomeuniqueproperties
of nanomaterials and also possibly induces new characteristics and functions based on
their synergetic effects. It provides a new dimension to design the next generation of
polymeric membranes with high performance and antifouling properties. The potential
applications of nanocomposite membranes could cover the whole filtration spectrum
including MF, UF, NF, RO, and FO. However, the practical application of
nanocompositemembranesforwatertreatmentisstillinitsinfancy.Moreworkisneeded
to evaluate the cost-effectiveness and long-term stability of nanocomposite membranes.
21.5.2 Adsorbents
Out of different processes, adsorption processes are widely used in water treatment
because of lower cost and effectiveness. Activated carbon has been found to be the
most important engineered adsorbent applied in water treatment, but because of high
cost, alternative adsorbents are being used. Almost all types of pollutants can be