Page 62 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 62
40 Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
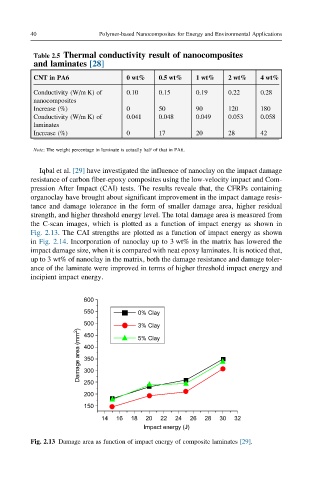
Table 2.5 Thermal conductivity result of nanocomposites
and laminates [28]
CNT in PA6 0 wt% 0.5 wt% 1 wt% 2 wt% 4 wt%
Conductivity (W/m K) of 0.10 0.15 0.19 0.22 0.28
nanocomposites
Increase (%) 0 50 90 120 180
Conductivity (W/m K) of 0.041 0.048 0.049 0.053 0.058
laminates
Increase (%) 0 17 20 28 42
Note: The weight percentage in laminate is actually half of that in PA6.
Iqbal et al. [29] have investigated the influence of nanoclay on the impact damage
resistance of carbon fiber-epoxy composites using the low-velocity impact and Com-
pression After Impact (CAI) tests. The results reveale that, the CFRPs containing
organoclay have brought about significant improvement in the impact damage resis-
tance and damage tolerance in the form of smaller damage area, higher residual
strength, and higher threshold energy level. The total damage area is measured from
the C-scan images, which is plotted as a function of impact energy as shown in
Fig. 2.13. The CAI strengths are plotted as a function of impact energy as shown
in Fig. 2.14. Incorporation of nanoclay up to 3 wt% in the matrix has lowered the
impact damage size, when it is compared with neat epoxy laminates. It is noticed that,
up to 3 wt% of nanoclay in the matrix, both the damage resistance and damage toler-
ance of the laminate were improved in terms of higher threshold impact energy and
incipient impact energy.
600
550 0% Clay
500 3% Clay
Damage area (mm 2 ) 400
450
5% Clay
350
300
250
200
150
14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32
Impact energy (J)
Fig. 2.13 Damage area as function of impact energy of composite laminates [29].