Page 636 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 636
Polymer nanocomposites for water treatments 587
Reaction involving valence band e .
%
TiO 2 (e )+O 2 !TiO 2 +O 2 (21.5)
% +
O 2 +H !HO 2 % (21.6)
%
TiO 2 (e )+HO 2 !TiO 2 +HO 2 (21.7)
+
%
TiO 2 (e )+O 2 +H !TiO 2 +H 2 O 2 (21.8)
TiO 2 (e )+H 2 O 2 !TiO 2 + OH+OH (21.9)
%
%
%
O 2 +H 2 O 2 ! OH+OH +O 2 (21.10)
% (21.11)
2HO 2 !O 2 +H 2 O 2
Photo holes have great potential to oxidize organic species directly or indirectly via
the combination with OH predominant in aqueous solutions:
%
R-H+ OH !R +H 2 O (21.12)
%
%
+
R-H+H !R !degradation products (21.13)
%
+
% % ), and peroxide radicals
Hydroxyl radicals ( OH), holes (h ), superoxide ions (O 2
( HO 2 ) are highly reactive intermediates that will oxidize a large variety of organic
%
compounds.
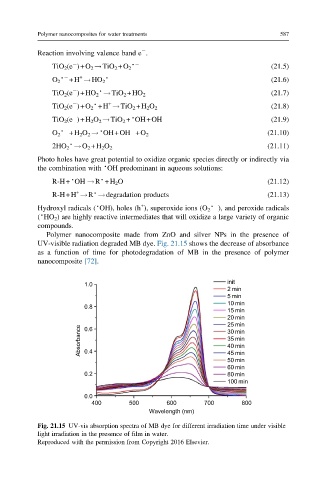
Polymer nanocomposite made from ZnO and silver NPs in the presence of
UV-visible radiation degraded MB dye. Fig. 21.15 shows the decrease of absorbance
as a function of time for photodegradation of MB in the presence of polymer
nanocomposite [72].
init
1.0
2 min
5 min
10 min
0.8
15 min
20 min
25 min
Absorbance 35 min
0.6
30 min
40 min
0.4
45 min
50 min
60 min
0.2 80 min
100 min
0.0
400 500 600 700 800
Wavelength (nm)
Fig. 21.15 UV-vis absorption spectra of MB dye for different irradiation time under visible
light irradiation in the presence of film in water.
Reproduced with the permission from Copyright 2016 Elsevier.