Page 122 - Power Electronic Control in Electrical Systems
P. 122
//SYS21/F:/PEC/REVISES_10-11-01/075065126-CH004.3D ± 110 ± [106±152/47] 17.11.2001 9:54AM
110 Power flows in compensation and control studies
where X TCSC is the equivalent reactance of the TCSC controller which may be
adjusted to regulate the transfer of active power across the TCSC, hence, P lm
reg
becomes P .
lm
4.2.3 The static phase shifter
The static phase shifter (SPS) varies the phase angles of the line end voltages with
little delay. This is achieved by injecting a voltage in quadrature with the line end
voltage at the sending end. This equipment may also be used to provide fast active
power flow regulation (Hingorani and Gyugyi, 2000).
The power flow model of the static phase shifter presented in this chapter is based
on the concept of a lossless transformer with complex taps. The control variable is a
phase angle, which is adjusted using Newton's algorithm to satisfy a specified active
power flow across the lossless transformer representing the static phase shifter
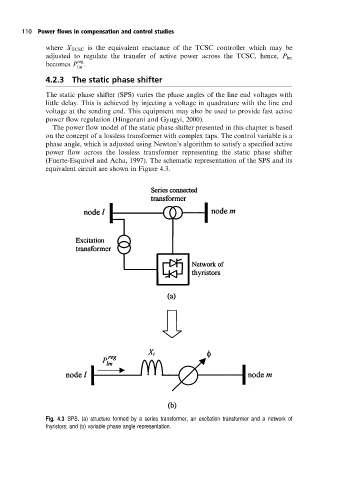
(Fuerte-Esquivel and Acha, 1997). The schematic representation of the SPS and its
equivalent circuit are shown in Figure 4.3.
Fig. 4.3 SPS. (a) structure formed by a series transformer, an excitation transformer and a networkof
thyristors; and (b) variable phase angle representation.