Page 123 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 123
116 Electromagnetic compatibility
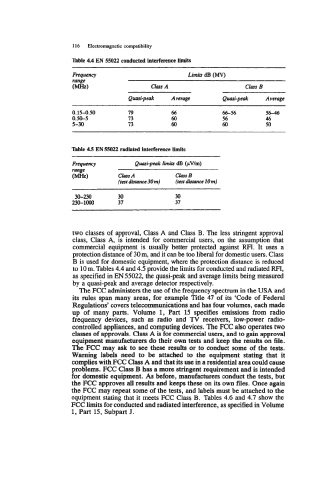
able 4.4 EN 55022 conducted interference limits
Fnqucney Limirr dB (Mv)
range
Claw A Class B
Quasi-peak Average Quasi-peak Average
0.15-0.50 79 66 66-56 56-46
0.%5 73 60 56 46
5-30 73 60 60 50
able 4.5 EN 55022 radiated interference limits
Fmlucncv Quasi-peak limits dB (pV/m)
range
(MHZ) Claw A Chs B
(tat distance 30 m) (rut distance 10 m)
30-230 30 30
230-1OOO 37 37
two classes of approval, Class A and Class B. The less stringent approval
class, Class A, is intended for commercial users, on the assumption that
commercial equipment is usually better protected against RFI. It uses a
protection distance of 30 m, and it can be too liberal for domestic users. Class
B is used for domestic equipment, where the protection distance is reduced
to 10 m. Tables 4.4 and 4.5 provide the limits for conducted and radiated RFI,
as specified in EN 55022, the quasi-peak and average limits being measured
by a quasi-peak and average detector respectively.
The FCC administers the use of the frequency spectrum in the USA and
its rules span many areas, for example Title 47 of its ‘Code of Federal
Regulations’ covers telecommunications and has four volumes, each made
up of many parts. Volume 1, Part 15 specifies emissions from radio
frequency devices, such as radio and TV receivers, low-power radio-
controlled appliances, and computing devices. The FCC also operates two
classes of approvals. Class A is for commercial users, and to gain approval
equipment manufacturers do their own tests and keep the results on file.
The FCC may ask to see these results or to conduct some of the tests.
Warning labels need to be attached to the equipment stating that it
complies with FCC Class A and that its use in a residential area could cause
problems. FCC Class B has a more stringent requirement and is intended
for domestic equipment. As before, manufacturers conduct the tests, but
the FCC approves all results and keeps these on its own files. Once again
the FCC may repeat some of the tests, and labels must be attached to the
equipment stating that it meets FCC Class B. Tables 4.6 and 4.7 show the
FCC limits for conducted and radiated interference, as specified in Volume
1, Part 15, Subpart J.