Page 13 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 13
6 Power semiconductor devices
A- Pull and rolaie mechanltm
M-
Growing crystal
000 flkseed crystal
Molten zone Silicon crystal Silica linei
Melt
healing
coil
AF
v
(E)
Ib) Graohite crucible
Crystal
0 RF heating coil
0
0
0 0
I
Silicon bar Meil I
(4
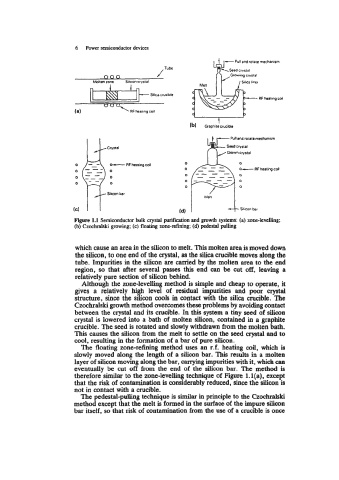
Figure 1.1 Semiconductor bulk crystal purification and growth systems: (a) zone-levelling;
(b) Czochralski growing; (c) floating zone-refining; (d) pedestal pulling
which cause an area in the silicon to melt. This molten area is moved down
the silicon, to one end of the crystal, as the silica crucible moves along the
tube. Impurities in the silicon are camed by the molten area to the end
region, so that after several passes this end can be cut off, leaving a
relatively pure section of silicon behind.
Although the zone-levelling method is simple and cheap to operate, it
gives a relatively high level of residual impurities and poor crystal
structure, since the silicon cools in contact with the silica crucible. The
Czochralski growth method overcomes these problems by avoiding contact
between the crystal and its crucible. In this system a tiny seed of silicon
crystal is lowered into a bath of molten silicon, contained in a graphite
crucible. The seed is rotated and slowly withdrawn from the molten bath.
This causes the silicon from the melt to settle on the seed crystal and to
cool, resulting in the formation of a bar of pure silicon.
The floating zone-refining method uses an r.f. heating coil, which is
slowly moved along the length of a silicon bar. This results in a molten
layer of silicon moving along the bar, carrying impurities with it, which can
eventually be cut off from the end of the silicon bar. The method is
therefore similar to the zone-levelling technique of Figure l.l(a), except
that the risk of contamination is considerably reduced, since the silicon is
not in contact with a crucible.
The pedestal-pulling technique is similar in principle to the Czochralski
method except that the melt is formed in the surface of the impure silicon
bar itself, so that risk of contamination from the use of a crucible is once