Page 131 - Power Electronics Handbook
P. 131
124 Power semiconductor protection
long arcing times, so that the inductive energy in the circuit is
dissipated in the arc;
(iii) Using lightning and other surge arrestors close to the equipment
being protected;
(iv) Placing a capacitor across the secondary of autotransformers, to
divide the voltage coupled from the primary due to the stray winding
capacitance.
5.3 Overvoltage protection
Three types of voltage suppressors are commonly used: those which store
the transient energy of the overvoltage and then dissipate it later as heat;
those which directly convert the energy of the overvoltage into heat, which
is then dissipated; and those which convert the overvoltage into an
overcurrent, and then use the techniques described in section 5.4 to protect
against it.
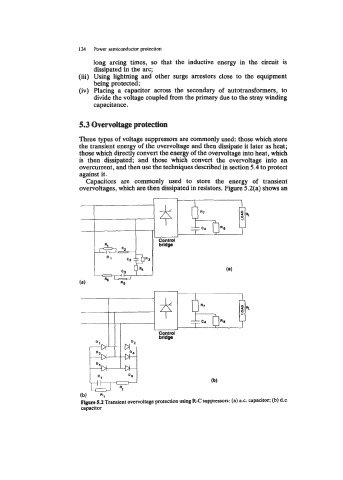
Capacitors are commonly used to store the energy of transient
overvoltages, which are then dissipated in resistors. Figure 5.2(a) shows an
(8)
9
(b)
(b) '1
F- 5.2 Transient overvoltage protection using R-C suppresson: (a) ax. capadtor; (b) d.c*
capacitor