Page 268 - Practical Machinery Management for Process Plants Major Process Equipment Maintenance and Repair
P. 268
250 Major Process Equipment Maintenance and Repair
S. S. SHAFT
H. S. SHAFT
Away from Pinion
-- Towards Gear
-~
~ ~ ~
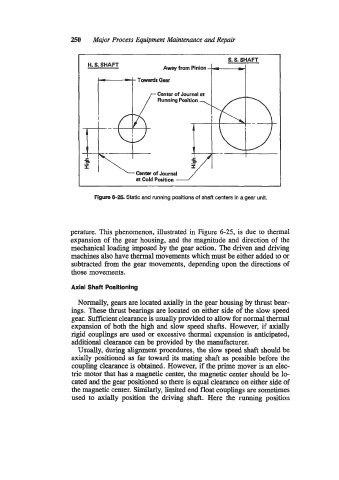
Figure 6-25. Static and running positions of shaft centers in a gear unit.
perature. This phenomenon, illustrated in Figure 6-25, is due to thermal
expansion of the gear housing, and the magnitude and direction of the
mechanical loading imposed by the gear action. The driven and driving
machines also have thermal movements which must be either added to or
subtracted from the gear movements, depending upon the directions of
those movements.
Axial Shaft Positioning
Normally, gears are located axially in the gear housing by thrust bear-
ings. These thrust bearings are located on either side of the slow speed
gear. Sufficient clearance is usually provided to allow for normal thermal
expansion of both the high and slow speed shafts. However, if axially
rigid couplings are used or excessive thermal expansion is anticipated,
additional clearance can be provided by the manufacturer.
Usually, during alignment procedures, the slow speed shaft should be
axially positioned as far toward its mating shaft as possible before the
coupling clearance is obtained. However, if the prime mover is an elec-
tric motor that has a magnetic center, the magnetic center should be lo-
cated and the gear positioned so there is equal clearance on either side of
the magnetic center. Similarly, limited end float couplings are sometimes
used to axially position the driving shaft. Here the running position