Page 42 - Practical Machinery Management for Process Plants Major Process Equipment Maintenance and Repair
P. 42
Installatiori, Maintenance, and Repair of Horizontal Pumps 27
RADIAL BEARING RADIAL BEARING
THRUST BEARING
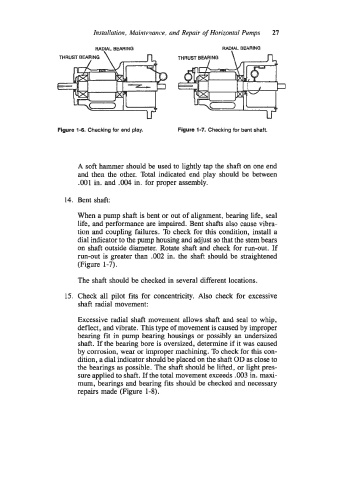
Figure 1-6. Checking for end play. Figure 1-7. Checking for bent shaft.
A soft hammer should be used to lightly tap the shaft on one end
and then the other. Total indicated end play should be between
.001 in. and .004 in. for proper assembly.
14. Bent shaft:
When a pump shaft is bent or out of alignment, bearing life, seal
life, and performance are impaired. Bent shafts also cause vibra-
tion and coupling failures. To check for this condition, install a
dial indicator to the pump housing and adjust so that the stem bears
on shaft outside diameter. Rotate shaft and check for run-out. If
run-out is greater than .002 in. the shaft should be straightened
(Figure 1-7).
The shaft should be checked in several different locations.
15. Check all pilot fits for concentricity. Also check for excessive
shaft radial movement:
Excessive radial shaft movement allows shaft and seal to whip,
deflect, and vibrate. This type of movement is caused by improper
bearing fit in pump bearing housings or possibly an undersized
shaft. If the bearing bore is oversized, determine if it was caused
by corrosion, wear or improper machining. To check for this con-
dition, a dial indicator should be placed on the shaft OD as close to
the bearings as possible. The shaft should be lifted, or light pres-
sure applied to shaft. If the total movement exceeds .003 in. maxi-
mum, bearings and bearing fits should be checked and necessary
repairs made (Figure 1-8).