Page 167 - Practical Well Planning and Drilling Manual
P. 167
Section 2 revised 11/00/bc 1/17/01 12:04 PM Page 143
2.1.5
Preliminary Work For the Drilling Program [ ]
Details. The third sheet shows how costs are arrived at for more com-
plex items. This shows what assumptions have been made for the esti-
mate. For instance, the cost per barrel of mud is matched against the
hole volume, assumed losses, and required surface volume to be built.
This is useful because if for instance it is decided to TD the well at a dif-
ferent depth, the depth on the Summary sheet is amended and then the
totals are automatically recalculated. Thus, it is very quick and easy to
revise the cost estimate when things change. New cost estimates can be
made by revising previous cost estimates by using a different cost mud,
inputting that cost, and updating the estimate.
In Figure 2-4, only the first few items are shown. The actual
spreadsheet shows logging, abandonment, and other costs.
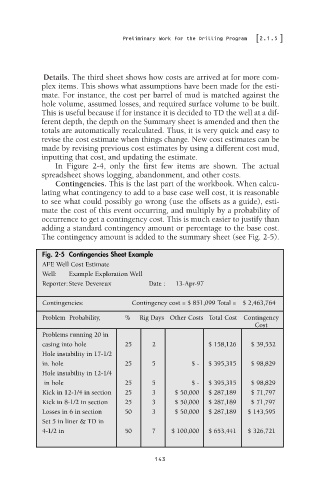
Contingencies. This is the last part of the workbook. When calcu-
lating what contingency to add to a base case well cost, it is reasonable
to see what could possibly go wrong (use the offsets as a guide), esti-
mate the cost of this event occurring, and multiply by a probability of
occurrence to get a contingency cost. This is much easier to justify than
adding a standard contingency amount or percentage to the base cost.
The contingency amount is added to the summary sheet (see Fig. 2-5).
Fig. 2-5 Contingencies Sheet Example
AFE Well Cost Estimate
Well: Example Exploration Well
Reporter:Steve Devereux Date : 13-Apr-97
Contingencies: Contingency cost = $ 851,099 Total = $ 2,463,764
Problem Probability, % Rig Days Other Costs Total Cost Contingency
Cost
Problems running 20 in
casing into hole 25 2 $ 158,126 $ 39,532
Hole instability in 17-1/2
in. hole 25 5 $ - $ 395,315 $ 98,829
Hole instability in 12-1/4
in hole 25 5 $ - $ 395,315 $ 98,829
Kick in 12-1/4 in section 25 3 $ 50,000 $ 287,189 $ 71,797
Kick in 8-1/2 in section 25 3 $ 50,000 $ 287,189 $ 71,797
Losses in 6 in section 50 3 $ 50,000 $ 287,189 $ 143,595
Set 5 in liner & TD in
4-1/2 in 50 7 $ 100,000 $ 653,441 $ 326,721
143