Page 320 - Pressure Swing Adsorption
P. 320
ii I
t MEMBRANE PROCESSES
PRESSURE SWING ADSORPTION
296 297
I
Dense Non-Porous
Active Laver
1000A
j_ I
T l
Porous Sublayer
~0.2mm
I
J_
Permeate Gas
Figure 8.5 Schemauc diagram solving construct100 of an asymmetric membrane.
Permeate
(c)
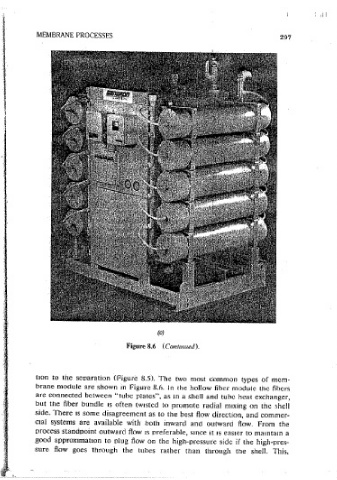
Figure 8.6 (Contmued).
(bi
t1on to the separation (Figure 8.5). The two most common types of mem-
brane module are shown rn Figure 8.6. J n the hollow fiber module the fibers
Hollow,
thin-walled are connected between ''tube plates", as rn ,1 .shell and tuhc heat exchanger,
porous tubes but the fiber bundle IS often twisted to promote radial mixing on the shell
side. There 1s some disagreement as to the best flow direction, and commer-
cial systems are available with both inward and outward flow. From the
process standpoint outward flow 1s preferable, smce 1t 1s easier to mamtam a
Retentate
good approx1mat10n to plug flow on the high-pressure side if the high-pres-
sure flow goes through the tubes rather than through the shell. This.
Figure 8.6 Membrane modules: (a) soiral wound, (b) hollow fiber type, and
.. lc)-~yw·"al "'ll?u-sr·•le ••nit-- (Cnur1~sy.0f now~Generon In.c.)