Page 221 - Principles and Applications of NanoMEMS Physics
P. 221
210 Chapter 5
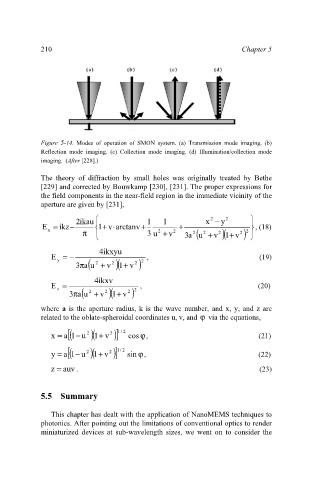
Figure 5-14. Modes of operation of SMON system. (a) Transmission mode imaging. (b)
Reflection mode imaging. (c) Collection mode imaging. (d) Illumination/collection mode
imaging. (After [228].)
The theory of diffraction by small holes was originally treated by Bethe
[229] and corrected by Bouwkamp [230], [231]. The proper expressions for
the field components in the near-field region in the immediate vicinity of the
aperture are given by [231],
°
°
E = ikz − 2 ikau ⋅arctan v + 1 1 + x 2 − y 2 ½
® + v1
¾ , (18)
π ° 3 u 2 + v 2 a 3 2 (u 2 + v 2 )( + v1 2 ) °
x
2
¯
¿
E = − 4 ikxyu , (19)
y 2 2 2 ) 2
3π a (u + v )( 1+ v
E = 4 ikxv , (20)
z ) 2
3π a (u + v 2 )( 1+ v 2
2
where a is the aperture radius, k is the wave number, and x, y, and z are
related to the oblate-spheroidal coordinates u, v, and ϕ via the equations,
1
x = a ( [ − u 2 )( + v 2 )] / 1 2 cos ϕ, (21)
1
y = a ( [ − u1 2 )( + v1 2 )] / 1 2 sin ϕ, (22)
z = auv . (23)
5.5 Summary
This chapter has dealt with the application of NanoMEMS techniques to
photonics. After pointing out the limitations of conventional optics to render
miniaturized devices at sub-wavelength sizes, we went on to consider the