Page 98 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 98
DESIGN OF CATALYSTS 85
TARGET REACTION
STOICHIOMETRIC ANALYSIS
SURFACE MECHANISM
REACTION PATH
CATALYST PROPERTIES
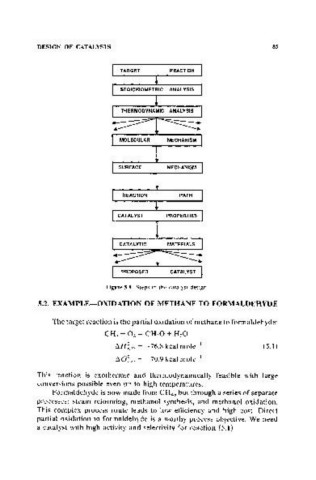
Figure 5.1. Steps in the catalyst design.
5.2. EXAMPLE-OXIDATION OF METHANE TO FORMALDEHYDE
The target reaction is the partial oxidation of methane to formaldehyde:
CH 4 + O 2 = CH 20 + H 20
t:..H~,25 = -76.8 kcal mole-I (5.1)
t:..G~.25 = -70.9 kcal mole-I
This reaction is exothermic and thermodynamically feasible with large
conversions possible even up to high temperatures.
Formaldehyde is now made from CH 4 , but through a series of separate
processes: steam reforming, methanol synthesis, and methanol oxidation.
This complex process route leads to low efficiency and high cost. Direct
partial oxidation to formaldehyde is a worthy process objective. We need
a catalyst with high activity and selectivity for reaction (5.1).