Page 138 - Process Equipment and Plant Design Principles and Practices by Subhabrata Ray Gargi Das
P. 138
5.4 Pinch design analysis 135
The design is completed by satisfying heating and cooling duties by utilising utilities away from
the pinch. A complete network is obtained by joining the hot and cold section configurations at the
pinch as shown in Fig. 5.7 and demonstrated in the design problems. Usually there are more than one
solutions for a real life problem.
While the tick off heuristic ensures minimum number of units, it does not necessarily guarantee
minimum utility requirement. In fact, it can sometimes result in excess utility, leading away from
minimum utility design. Utilisation of excessive temperature difference in pinch exchangers, leaving
too little driving force for exchangers elsewhere in the network may lead to this. If this arises, a
different set of pinch matches can be tried or the duty on the pinch exchanger can be reduced leading to
more than the minimum number of units.
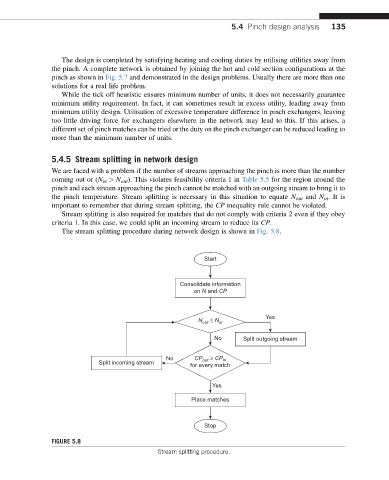
5.4.5 Stream splitting in network design
We are faced with a problem if the number of streams approaching the pinch is more than the number
coming out or (N in > N out ). This violates feasibility criteria 1 in Table 5.5 for the region around the
pinch and each stream approaching the pinch cannot be matched with an outgoing stream to bring it to
the pinch temperature. Stream splitting is necessary in this situation to equate N out and N in .It is
important to remember that during stream splitting, the CP inequality rule cannot be violated.
Stream splitting is also required for matches that do not comply with criteria 2 even if they obey
criteria 1. In this case, we could split an incoming stream to reduce its CP.
The stream splitting procedure during network design is shown in Fig. 5.8.
Start
Consolidate information
on N and CP
Yes
N out ≤ N in
No Split outgoing stream
No CP out ≥ CP in
Split incoming stream
for every match
Yes
Place matches
Stop
FIGURE 5.8
Stream splitting procedure.