Page 206 - Process Modelling and Simulation With Finite Element Methods
P. 206
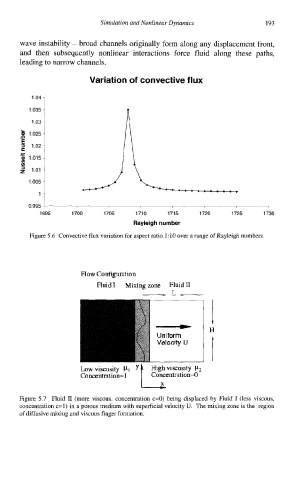
Simulation and Nonlinear Dynamics 193
wave instability - broad channels originally form along any displacement front,
and then subsequently nonlinear interactions force fluid along these paths,
leading to narrow channels.
Variation of convective flux
I
1.04 -
1.035
1.03
?8
n 1.025 ~
-
E
3 1.02
C
-
1.015 -
v)
2 1.01
!
’!
0.995 c-- 7- TI-- v-, 1
1695 1700 1705 1710 1715 1720 1725 1730
Rayleigh number
Figure 5.6 Convective flux variation for aspect ratio 1: 10 over a range of Rayleigh numbers
Flow Configuration
Fluid I Mixing zone Fluid lI
-L-
t
Lowviscosity PI y Highviscosity FL2
Cancenlralion= 1 Concentration=O
Figure 5.7 Fluid II (more viscous, concentration c=O) being displaced by Fluid I (less viscous,
concentration c=l) in a porous medium with superficial velocity U. The mixing zone is the region
of diffusive mixing and viscous finger formation.