Page 72 - Programming the Photon Getting Started With the Internet of Things
P. 72
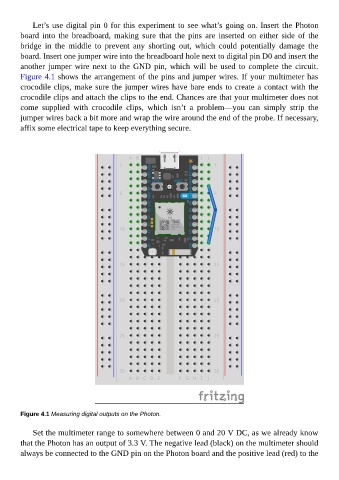
Let’s use digital pin 0 for this experiment to see what’s going on. Insert the Photon
board into the breadboard, making sure that the pins are inserted on either side of the
bridge in the middle to prevent any shorting out, which could potentially damage the
board. Insert one jumper wire into the breadboard hole next to digital pin D0 and insert the
another jumper wire next to the GND pin, which will be used to complete the circuit.
Figure 4.1 shows the arrangement of the pins and jumper wires. If your multimeter has
crocodile clips, make sure the jumper wires have bare ends to create a contact with the
crocodile clips and attach the clips to the end. Chances are that your multimeter does not
come supplied with crocodile clips, which isn’t a problem—you can simply strip the
jumper wires back a bit more and wrap the wire around the end of the probe. If necessary,
affix some electrical tape to keep everything secure.
Figure 4.1 Measuring digital outputs on the Photon.
Set the multimeter range to somewhere between 0 and 20 V DC, as we already know
that the Photon has an output of 3.3 V. The negative lead (black) on the multimeter should
always be connected to the GND pin on the Photon board and the positive lead (red) to the