Page 93 - Programming the Raspberry Pi Getting Started with Python
P. 93
relay also has an LED that lights when the relay is activated. There are also two LEDs that can be
controlled independently. Four of the inputs have push switches next to them.
The Pi Face has its own Python module that simplifies the use of the board. The following example
entered into the Python console shows you how to read digital input 2:
To turn on digital output 2, you would do the following:
The LEDs and relays have their own control functions. The following example turns LED 1 on then
off again and then turns Relay 1 on:
The library must be downloaded and installed. For downloads, documentation, and some sample
projects, visit the projects code page at https://github.com/thomasmacpherson/piface. You can also
find more information about the project at http://pi.cs.man.ac.uk/interface.htm.
Slice of PI/O
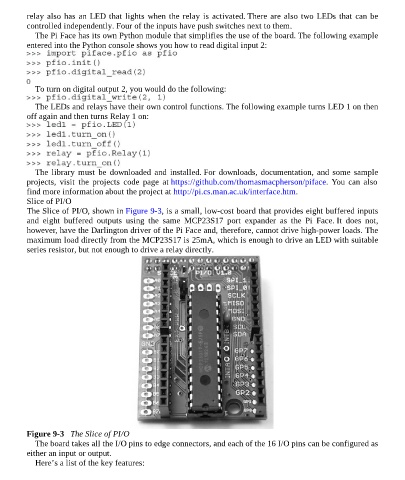
The Slice of PI/O, shown in Figure 9-3, is a small, low-cost board that provides eight buffered inputs
and eight buffered outputs using the same MCP23S17 port expander as the Pi Face. It does not,
however, have the Darlington driver of the Pi Face and, therefore, cannot drive high-power loads. The
maximum load directly from the MCP23S17 is 25mA, which is enough to drive an LED with suitable
series resistor, but not enough to drive a relay directly.
Figure 9-3 The Slice of PI/O
The board takes all the I/O pins to edge connectors, and each of the 16 I/O pins can be configured as
either an input or output.
Here’s a list of the key features: