Page 165 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 165
150 Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
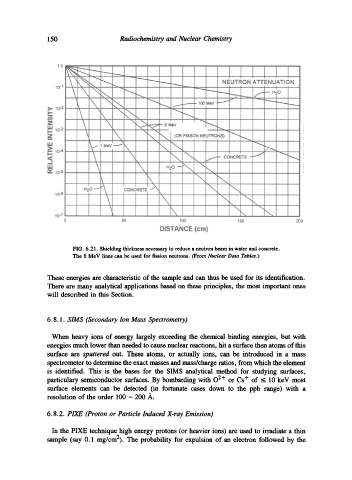
FIG. 6.2 I. Shielding thickness necessary to reduce a neutron beam in water and concrete.
The 6 MeV lines can be used for fission neutrons. (From Nuclear Data Tables.)
These energies are characteristic of the sample and can thus be used for its identification.
There are many analytical applications based on these principles, the most important ones
will described in this Section.
6.8.1. SIMS (Secorutary Ion Mass Spectrometry)
When heavy ions of energy largely exceeding the chemical binding energies, but with
energies much lower than needed to cause nuclear reactions, hit a surface then atoms of this
surface are sputtered out. These atoms, or actually ions, can be introduced in a mass
spectrometer to determine the exact masses and mass/charge ratios, from which the dement
is identified. This is the bases for the SIMS analytical method for studying surfaces,
particulary semiconductor surfaces. By bombarding with 0 2 + or Cs + of _ 10 keV most
surface dements can be detected (in fortunate cases down to the ppb range) with a
resolution of the order 100 - 200 A.
6.8.2. PIXE (Proton or Particle Induced X-ray Emission)
In the PIXE technique high energy protons (or heavier ions) are used to irradiate a thin
sample (say 0.1 mg/cm2). The probability for expulsion of an electron followed by the