Page 26 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 26
Nuclei, Isotopes and Isotope Separation 15
EI~ n = ~hmv 2 = qV (2.5)
joule (or newton meter). If q is given in units of the elementary charge, the kinetic energy
is in units of electron volts (eV). For transformation to other energy units, see Appendix
IV.
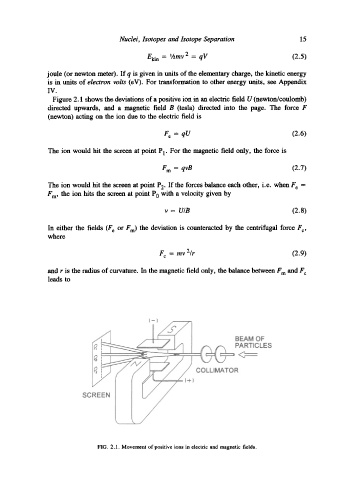
Figure 2.1 shows the deviations of a positive ion in an electric field U (newton/coulomb)
directed upwards, and a magnetic field B (tesla) directed into the page. The force F
(newton) acting on the ion due to the electric field is
F e = qU (2.6)
The ion would hit the screen at point PI" For the magnetic field only, the force is
F m = qvB (2.7)
The ion would hit the screen at point P2" If the forces balance each other, i.e. when F e =
F m, the ion hits the screen at point P0 with a velocity given by
v = U/B (2.8)
In either the fields (F e or Fm) the deviation is counteracted by the centrifugal force F c,
where
F c = mv2/r (2.9)
and r is the radius of curvature. In the magnetic field only, the balance between F m and F c
leads to
FIG. 2.1. Movement of positive ions in electric and magnetic fields.