Page 27 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 27
16 Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
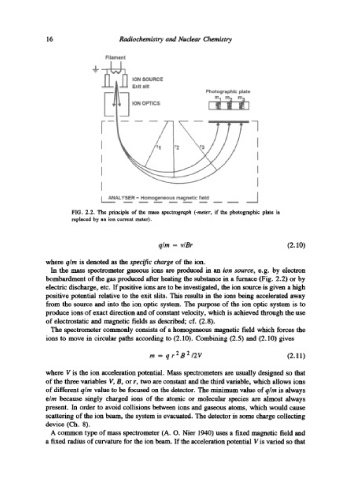
FIG. 2.2. The principle of the mass spectrograph (-meter, if the photographic plate is
replaced by an ion current meter).
q/m = v/Br (2.10)
where q/m is denoted as the specific charge of the ion.
In the mass spectrometer gaseous ions are producexl in an ion source, e.g. by electron
bombardment of the gas produced after heating the substance in a furnace (Fig. 2.2) or by
electric discharge, etc. If positive ions are to be investigated, the ion source is given a high
positive potential relative to the exit slits. This results in the ions being accelerated away
from the source and into the ion optic system. The purpose of the ion optic system is to
produce ions of exact direction and of constant velocity, which is achieved through the use
of electrostatic and magnetic fields as described; cf. (2.8).
The spectrometer commonly consists of a homogeneous magnetic field which forces the
ions to move in circular paths according to (2.10). Combining (2.5) and (2.10) gives
m = q r 2B2/2V (2.11)
where V is the ion acceleration potential. Mass spectrometers are usually designed so that
of the thre~ variables V, B, or r, two are constant and the third variable, which allows ions
of different q/m value to be focused on the detector. The minimum value of q/m is always
e/m because singly charged ions of the atomic or molecular species are almost always
present. In order to avoid collisions between ions and gaseous atoms, which would cause
scattering of the ion beam, the system is evacuated. The detector is some charge collecting
device (Ch. 8).
A common type of mass spectrometer (A. O. Nier 1940) uses a fixed magnetic field and
a fixed radius of curvature for the ion beam. If the acceleration potential V is varied so that