Page 261 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 261
Uses of Radioactive Tracers 245
D'= D C (9.2)
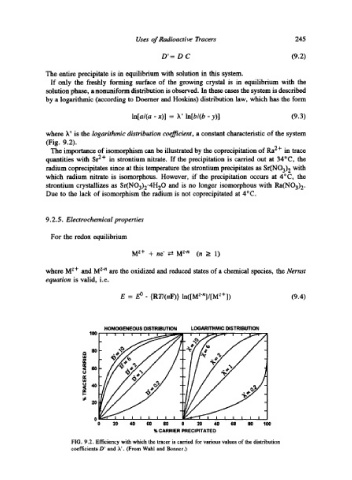
The entire precipitate is in equilibrium with solution in this system.
If only the freshly forming surface of the growing crystal is in equilibrium with the
solution phase, a nonuniform distribution is observed. In these cases the system is described
by a logarithmic (according to Doemer and Hoskins) distribution law, which has the form
In[a/(a - x)] = k' ln[b/(b - y)] (9.3)
where k' is the logarithmic distribution coefficient, a constant characteristic of the system
(Fig. 9.2).
The importance of isomorphism can be illustrated by the coprecipitation of Ra 2 + in trace
quantities with Sr 2+ in strontium nitrate. If the precipitation is carried out at 34~ the
radium coprecipitates since at this temperature the strontium precipitates as St(NO3) 2 with
which radium nitrate is isomorphous. However, if the precipitation occurs at 40C, the
strontium crystallizes as Sr(NO3)2.4H20 and is no longer isomorphous with Ra(NO3) 2.
Due to the lack of isomorphism the radium is not coprecipitated at 4~
9.2.5. Electrochemical properties
For the redox equilibrium
M z+ +ne-~-M z-n (n > 1)
where M z + and M z-n are the oxidized and reduced states of a chemical species, the Nernst
equation is valid, i.e.
E = E ~ {RT/(nF)} ln([Mz-n]/[MZ+]) (9.4)
HOMOGENEOUS DISTRIBUTION LOGARITHMIC DISTRIBUTION
.
zO
0
0 20 40 60 80 0 20 40 60 81) 100
% CARRIER PRECIPITATED
FIG. 9.2. Efficiency with which the tracer is carried for various values of the distribution
coefficients D' and h'. (From Wahl and Bonner.)