Page 25 - Rapid Learning in Robotics
P. 25
2.1 Actuation: The Puma Robot 11
... Host Host Host Host Host Host ...
(SGI Pool) (Sun Pool) (IBM Pool) (DEC Pool) (NeXT Pool) (PC Pool)
LAN Ethernet
"druide" "argus"
Host Host Active Pipeline
(SUN Sparc 2) 3D Space- 3D Space- (SUN Sparc 20) Image
Mouse Mouse Camera Processing
System (Datacube)
"manus" S-bus / VME
Controller
( 68040) VME-Bus
S-bus / VME
VME-Bus
Parallel Port M-module Interface
~ Timer
~
Parallel Port
DLR
BusMaster BRAD A/D D/A Digital DSP
DA
DSP
conv conv ports Image
image
PUMA conv Processing
processing
LSI 11 Robot ~ ~ ~ ~ (Androx)
(Androx)
Controller ~ ~ Light
6 DOF
6503 ~
Force/ Fingertip Presssure Life-Bit
Torque /Position Motor
motor
motor
Motor Wrist Tactile Sensors Driver Laser
motor
motor
motor
motor
Drivers + Sensor Sensors driver driver
driver
driver
Light
Sensor driver driver Light
Interfaces
Wrist Tactile Image
Manipulator Hydraulic Hand Misc.
Sensor Sensors Processing
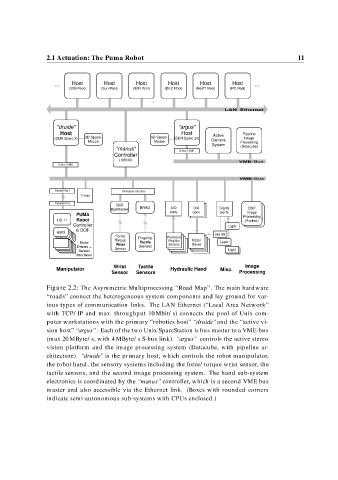
Figure 2.2: The Asymmetric Multiprocessing “Road Map”. The main hardware
“roads” connect the heterogeneous system components and lay ground for var-
ious types of communication links. The LAN Ethernet (“Local Area Network”
with TCP/IP and max. throughput 10 Mbit/s) connects the pool of Unix com-
puter workstations with the primary “robotics host” “druide” and the “active vi-
sion host” “argus” . Each of the two Unix SparcStation is bus master to a VME-bus
(max 20 MByte/s, with 4 MByte/s S-bus link). “argus” controls the active stereo
vision platform and the image processing system (Datacube, with pipeline ar-
chitecture). “druide” is the primary host, which controls the robot manipulator,
the robot hand, the sensory systems including the force/torque wrist sensor, the
tactile sensors, and the second image processing system. The hand sub-system
electronics is coordinated by the “manus” controller, which is a second VME bus
master and also accessible via the Ethernet link. (Boxes with rounded corners
indicate semi-autonomous sub-systems with CPUs enclosed.)