Page 408 - Reciprocating Compressors Operation Maintenance
P. 408
Reciprocating Compressor Calculations 393
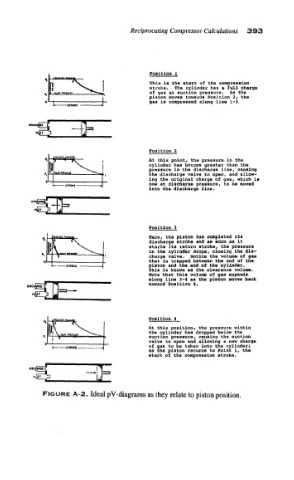
Position 1
This is the start of the compression
stroke. The cylinder has a full charge
of gas at auction pressure. AS the
piston moves towards Position 2, the
gas is compressed along line 1-2,
Position 2
At this point, the pressure in the
cylinder has become greater than the
pressure in the discharge line, causing
the discharge valve to open, and allow-
ing the original charge of gas, which is
now at discharge pressure, to be moved
into the discharge line.
Position 3
Here, the piston has completed its
discharge stroke and as soon as it
starts its return stroke, the pressure
in the cylinder drops, cloving the dis-
charge valve. Notice the volume of ga,s
that is trapped between the end of the
piston and the end of the cylinder,
This is known as the clearance volume.
Note that this volume of gas expands
along line 3-4 as the piston moves back
toward Position 4.
Position 4
At this position, the pressure within
the cylinder has dropped below the
suction pressure, causing the auction
valve to open and allowing a new charge
of gas to be taken into the cylinder;
as the piston returns to Point 1, the
start of the compression stroke.
FIGURE A-2. Ideal pV-diagrams as they relate to piston position.