Page 349 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 349
Pretreatment of agroindustry waste by ozonolysis for synthesis of biorefinery products 317
industrial chemicals, opening it up for even more applications. The use of cellulose
as a material is already well established in the textile and plastics sectors, but the
transformation of cellulose into other chemicals is a relatively new field. This sec-
tion will focus on some of the high-value cellulose-derived chemicals derived from
lignocellulosic biomass waste.
14.3.1 Bioethanol
Bioethanol is one of the high-potential products from agroindustry wastes that are
unlocked by the pretreatment method. The second-generation ethanol production
needs a pretreatment step in order to degrade the lignin and thereby getting a rea-
sonable sugar release yield (Garcı ´a-Cubero et al., 2009; Travaini et al., 2016a,b).
Many types of pretreatment methods have been used by utilizing agroindustry waste
as the raw material for bioethanol production. Among the agroindustry wastes that
have been utilized are sugarcane bagasse (Travaini et al., 2016a), cotton stalks
(Kaur et al., 2012), and wheat straw (Bellido et al., 2013) as summarized in
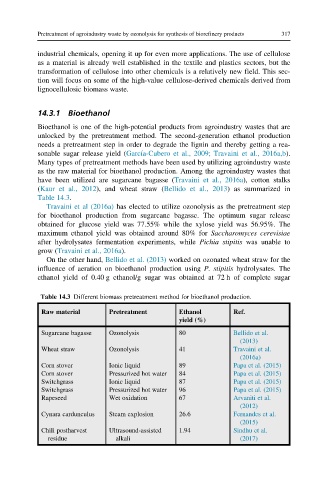
Table 14.3.
Travaini et al (2016a) has elected to utilize ozonolysis as the pretreatment step
for bioethanol production from sugarcane bagasse. The optimum sugar release
obtained for glucose yield was 77.55% while the xylose yield was 56.95%. The
maximum ethanol yield was obtained around 80% for Saccharomyces cerevisiae
after hydrolysates fermentation experiments, while Pichia stipitis was unable to
grow (Travaini et al., 2016a).
On the other hand, Bellido et al. (2013) worked on ozonated wheat straw for the
influence of aeration on bioethanol production using P. stipitis hydrolysates. The
ethanol yield of 0.40 g ethanol/g sugar was obtained at 72 h of complete sugar
Table 14.3 Different biomass pretreatment method for bioethanol production.
Raw material Pretreatment Ethanol Ref.
yield (%)
Sugarcane bagasse Ozonolysis 80 Bellido et al.
(2013)
Wheat straw Ozonolysis 41 Travaini et al.
(2016a)
Corn stover Ionic liquid 89 Papa et al. (2015)
Corn stover Pressurized hot water 84 Papa et al. (2015)
Switchgrass Ionic liquid 87 Papa et al. (2015)
Switchgrass Pressurized hot water 96 Papa et al. (2015)
Rapeseed Wet oxidation 67 Arvaniti et al.
(2012)
Cynara cardunculus Steam explosion 26.6 Fernandes et al.
(2015)
Chili postharvest Ultrasound-assisted 1.94 Sindhu et al.
residue alkali (2017)