Page 109 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 109
98 Reliability and Maintainability of In-Service Pipelines
accounts for missing points utilizing pattern recognition. Zhou et al. (2009) devel-
oped a pipe condition ranking method using a heuristic outranking method that
constructs an outranking relation for a particular criterion and uses this relation to
give ranks to each pipe.
A main difference between the heuristic models and other deterioration models
is incorporating engineering knowledge rather than data parameters that affect a
pipe. This procedure can be considered as a reliable method to illustrate failure
risks with limited or no pipe data. However, application of this methodology is lim-
ited due to its simplicity and the fact that any type of pipe material can be analyzed.
In general, heuristic models can be used as a first step in the determination of fail-
ure rates if no other mathematical models are available (Clair and Sinha 2012).
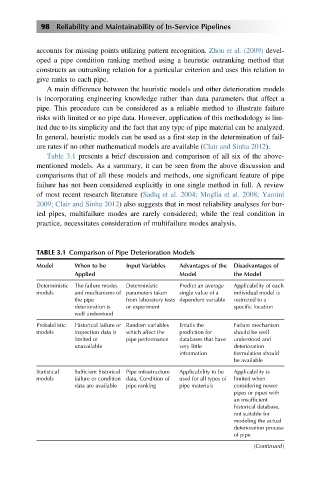
Table 3.1 presents a brief discussion and comparison of all six of the above-
mentioned models. As a summary, it can be seen from the above discussion and
comparisons that of all these models and methods, one significant feature of pipe
failure has not been considered explicitly in one single method in full. A review
of most recent research literature (Sadiq et al. 2004; Moglia et al. 2008; Yamini
2009; Clair and Sinha 2012) also suggests that in most reliability analyses for bur-
ied pipes, multifailure modes are rarely considered; while the real condition in
practice, necessitates consideration of multifailure modes analysis.
TABLE 3.1 Comparison of Pipe Deterioration Models
Model When to be Input Variables Advantages of the Disadvantages of
Applied Model the Model
Deterministic The failure modes Deterministic Predict an average Applicability of each
models and mechanisms of parameters taken single value of a individual model is
the pipe from laboratory tests dependent variable restricted to a
deterioration is or experiment specific location
well understood
Probabilistic Historical failure or Random variables Entails the Failure mechanism
models inspection data is which affect the prediction for should be well
limited or pipe performance databases that have understood and
unavailable very little deterioration
information formulation should
be available
Statistical Sufficient historical Pipe infrastructure Applicability to be Applicability is
models failure or condition data, Condition of used for all types of limited when
data are available pipe ranking pipe materials considering newer
pipes or pipes with
an insufficient
historical database,
not suitable for
modeling the actual
deterioration process
of pipe
(Continued )