Page 110 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 110
Methods for Structural Reliability Analysis 99
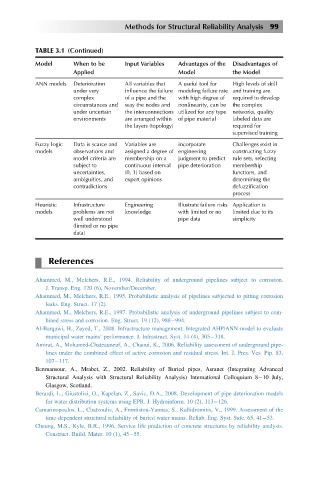
TABLE 3.1 (Continued)
Model When to be Input Variables Advantages of the Disadvantages of
Applied Model the Model
ANN models Deterioration All variables that A useful tool for High levels of skill
under very influence the failure modeling failure rate and training are
complex of a pipe and the with high degree of required to develop
circumstances and way the nodes and nonlinearity, can be the complex
under uncertain the interconnections utilized for any type networks, quality
environments are arranged within of pipe material labeled data are
the layers (topology) required for
supervised training
Fuzzy logic Data is scarce and Variables are incorporate Challenges exist in
models observations and assigned a degree of engineering constructing fuzzy
model criteria are membership on a judgment to predict rule sets, selecting
subject to continuous interval pipe deterioration membership
uncertainties, (0, 1) based on functions, and
ambiguities, and expert opinions determining the
contradictions defuzzification
process
Heuristic Infrastructure Engineering Illustrate failure risks Application is
models problems are not knowledge with limited or no limited due to its
well understood pipe data simplicity
(limited or no pipe
data)
References
Ahammed, M., Melchers, R.E., 1994. Reliability of underground pipelines subject to corrosion.
J. Transp. Eng. 120 (6), November/December.
Ahammed, M., Melchers, R.E., 1995. Probabilistic analysis of pipelines subjected to pitting corrosion
leaks. Eng. Struct. 17 (2).
Ahammed, M., Melchers, R.E., 1997. Probabilistic analysis of underground pipelines subject to com-
bined stress and corrosion. Eng. Struct. 19 (12), 988 994.
Al-Barqawi, H., Zayed, T., 2008. Infrastructure management: Integrated AHP/ANN model to evaluate
municipal water mains’ performance. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 14 (4), 305 318.
Amirat, A., Mohamed-Chateauneuf, A., Chaoui, K., 2006. Reliability assessment of underground pipe-
lines under the combined effect of active corrosion and residual stress. Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip. 83,
107 117.
Benmansour, A., Mrabet, Z., 2002. Reliability of Buried pipes, Asranet (Integrating Advanced
Structural Analysis with Structural Reliability Analysis) International Colloquium 8 10 July,
Glasgow, Scotland.
Berardi, L., Giustolisi, O., Kapelan, Z., Savic, D.A., 2008. Development of pipe deterioration models
for water distribution systems using EPR. J. Hydroinform. 10 (2), 113 126.
Camarinopoulos, L., Chatzoulis, A., Frontistou-Yannas, S., Kallidromitis, V., 1999. Assessment of the
time-dependent structural reliability of buried water mains. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe. 65, 41 53.
Cheung, M.S., Kyle, B.R., 1996. Service life prediction of concrete structures by reliability analysis.
Construct. Build. Mater. 10 (1), 45 55.